Flexographic Printing Machine Developments Highlight Integrated Mechanical Solutions
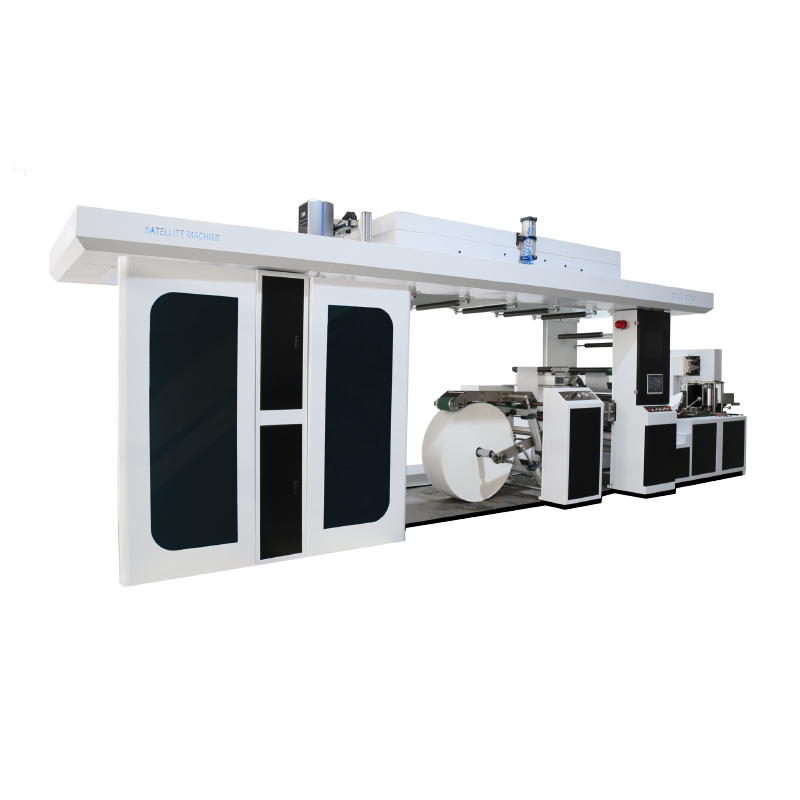
The flexographic printing machine has become an important part of the packaging and labeling industries, offering adaptable solutions for printing on paper, cardboard, plastic films, and other flexible substrates. This development includes the integration of CI flexo printing machine designs, micro motor functions, gearbox mechanisms, and reducers, all working together to create reliable printing systems.
Flexo printing machines operate on the principle of flexible relief plates, transferring ink onto a wide range of materials at high speeds. To maintain steady performance, motors play a critical role in ensuring that rollers and plates function in precise coordination. Vertical and horizontal motor alignments, supported by advanced designs, allow for smoother print registration and reduced mechanical stress. In large-scale production, this translates into consistent color application and dependable machine operation.
The CI flexo printing machine, or central impression type, represents another development in this sector. By mounting multiple print stations around a single impression drum, CI designs enable precise alignment of different colors. This configuration demands accurate speed control and stable torque to maintain registration across all units. The role of integrated motor systems, supported by magnetic and mechanical enhancements, is crucial in achieving smooth transitions and consistent output for packaging materials that require multicolor designs.

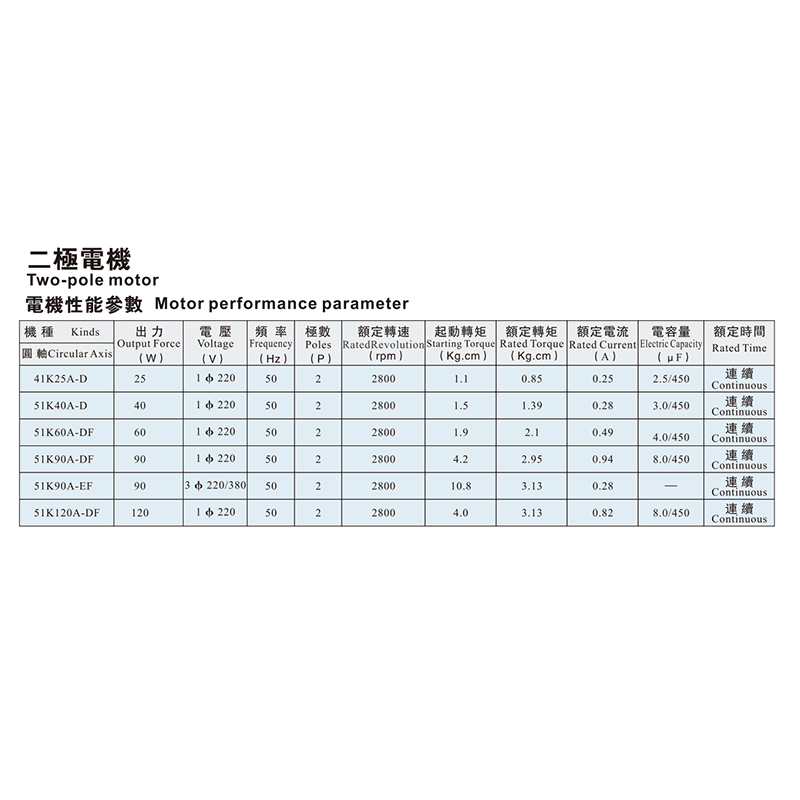
Micro motors also play an essential role within flexographic printing systems. While main motors drive the larger components, micro motors are often applied to auxiliary functions such as tension adjustment, web guiding, or precise roller positioning. Their small size and focused output allow for incremental control, which enhances the accuracy of print jobs.
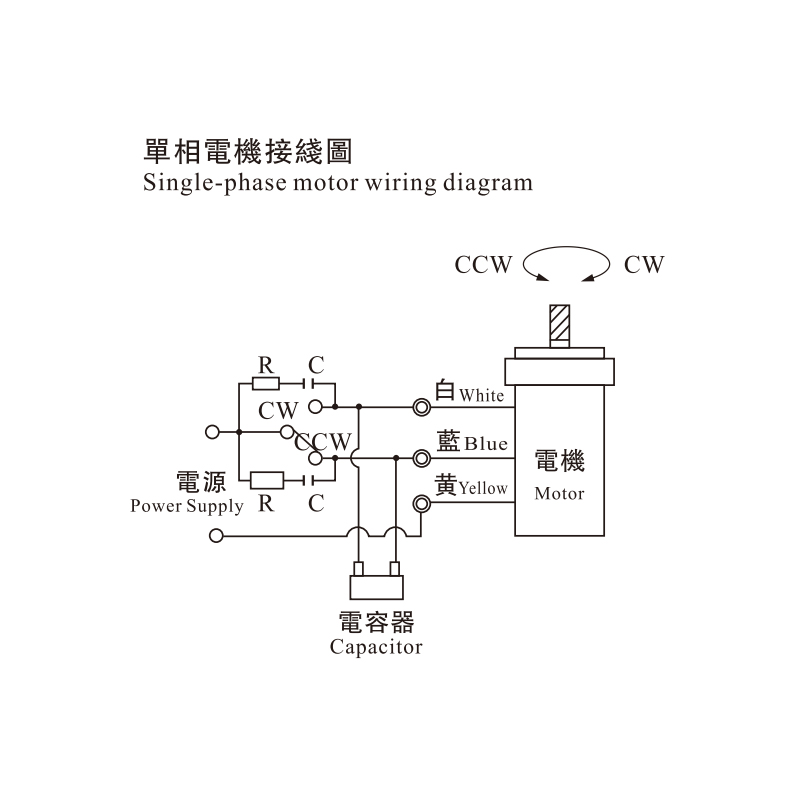
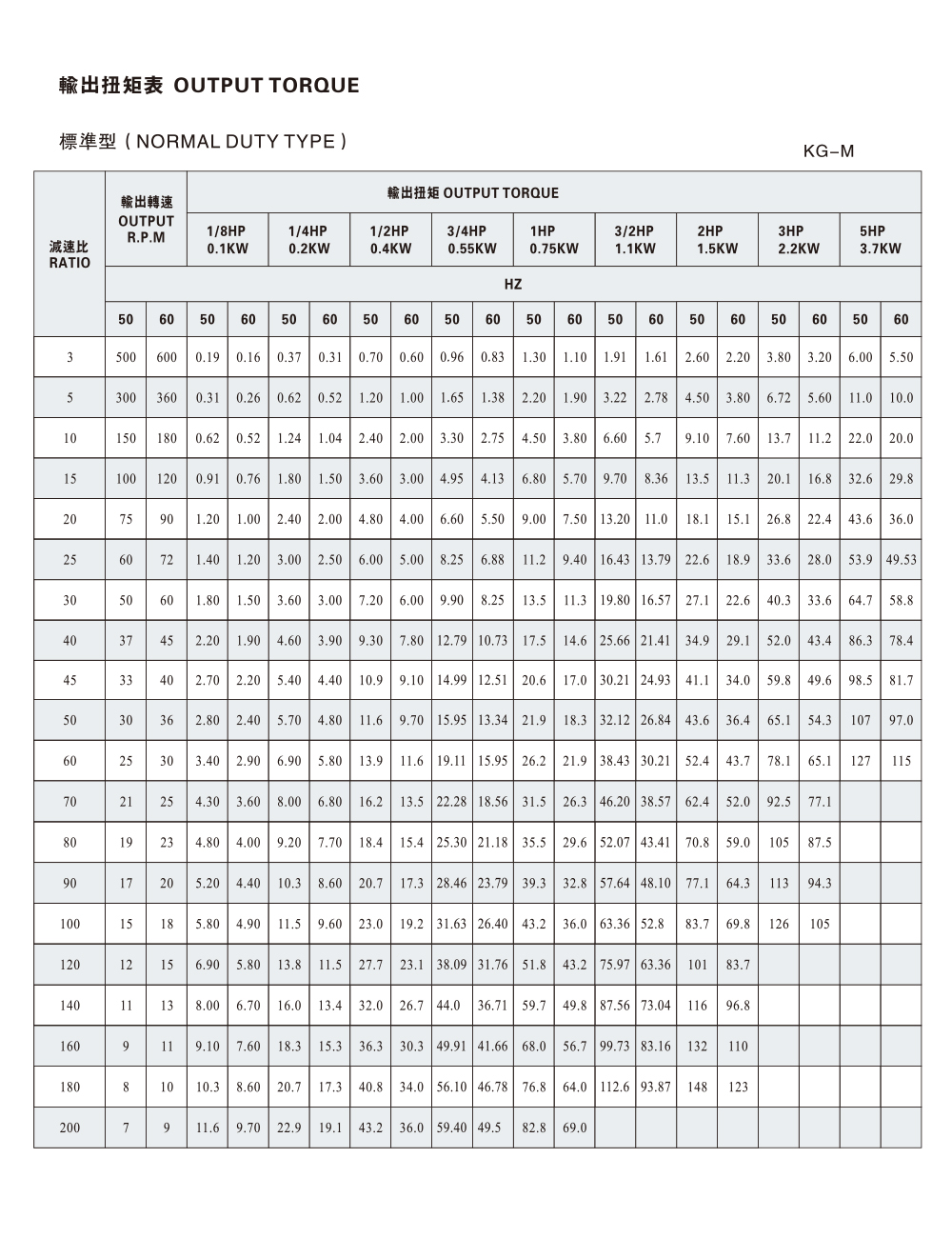
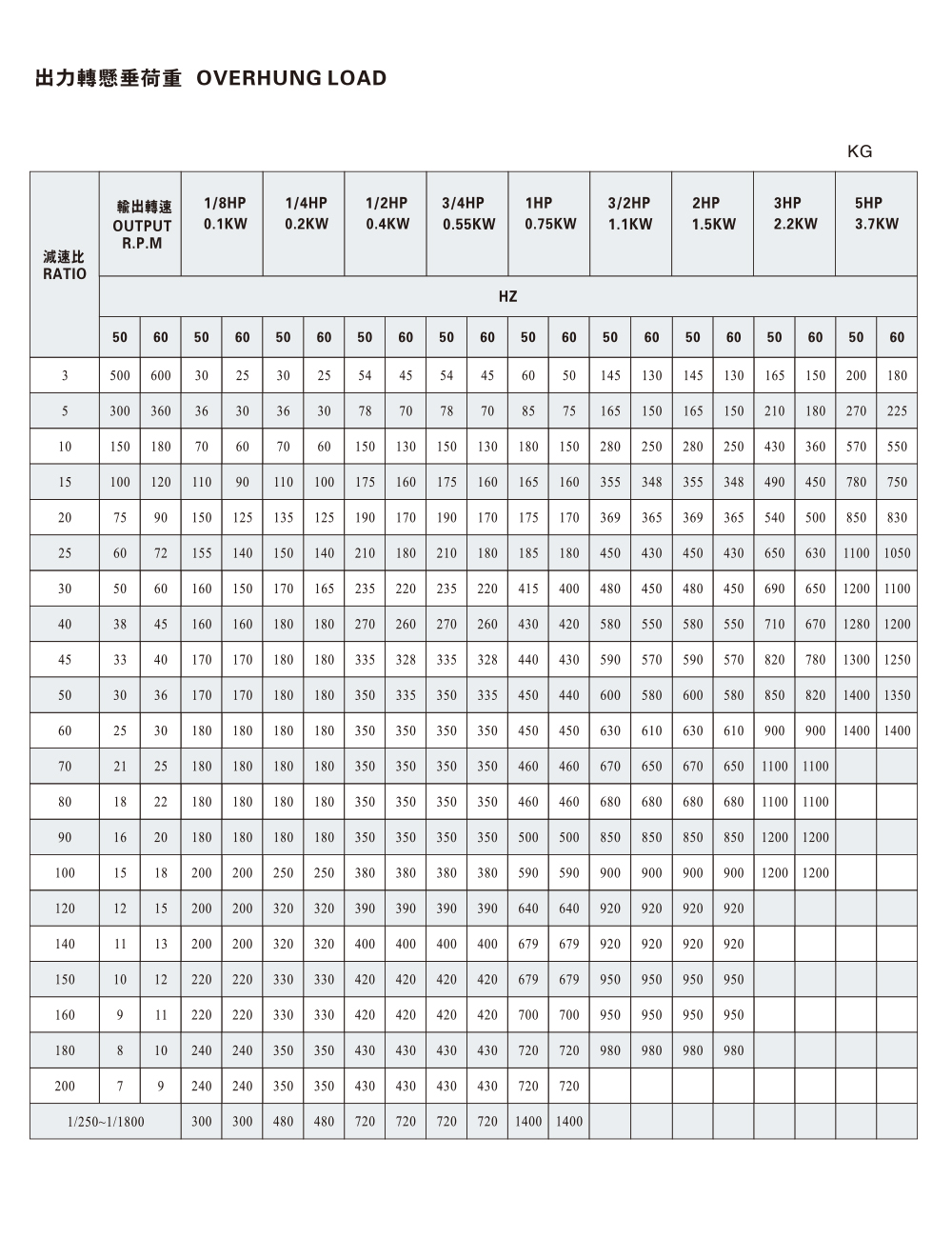
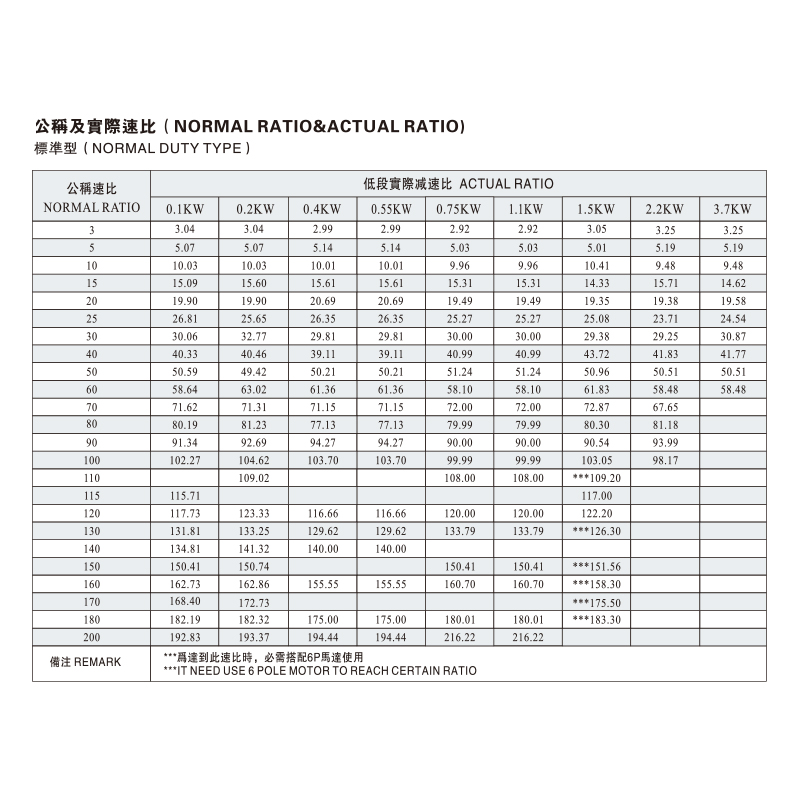
Another key part of flexographic printing machine design is the gear box. Acting as a mediator between motors and driven components, gear boxes regulate speed and torque to match operational demands. In flexographic printing, this ensures that rollers move at controlled speeds, reducing slippage and supporting uniform ink transfer. Gear boxes also provide versatility, allowing machines to handle a variety of substrates by adjusting rotational force without redesigning the motor system.
Reducers complement gear boxes by focusing on energy management and torque distribution. Their function is to reduce motor speed while increasing torque, which is particularly valuable in large printing machines that handle heavy rolls of substrate. In addition, reducers reduce wear on components by distributing load more evenly, which contributes to long-term reliability in high-volume operations.
The combination of these elements—CI flexo printing machines, micro motors, gear boxes, and reducers—demonstrates the interconnected nature of printing equipment design. Each part contributes to the overall balance of efficiency, durability, and performance. Flexo printing machines require precise synchronization, and this is achieved not through a single innovation but through the coordinated function of multiple mechanical and electrical systems.
Looking ahead, the integration of mechanical and electrical components in flexographic printing machines will remain a focus for the printing industry. CI designs will continue to support multicolor applications, micro motors will expand control functions, and gear boxes with reducers will ensure consistent power management. The steady improvement of these systems illustrates how industrial engineering contributes to reliable printing performance across packaging and labeling sectors.
The development of the flexographic printing machine highlights a broader trend of applying advanced mechanical solutions to achieve efficiency and adaptability in production.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى










Contact Us