Motor Applications Enhance Reliability in Printing Machinery
The role of the motor in industrial machinery has become increasingly significant, particularly in sectors such as packaging and labeling. Within the printing field, the flexo printing machine and CI flexo printing machine rely on motors to provide consistent motion, energy transfer, and stability during long production runs. Motors, together with supporting components such as the micro motor, gearbox, and reducer, form the mechanical foundation that ensures accurate and dependable operation.
In flexo printing machines, motors provide the driving force required to rotate printing cylinders and manage substrate feed. The function is not limited to delivering energy; it also involves maintaining precise speed control across multiple units. This synchronization is vital for achieving even ink distribution and alignment of print patterns. Without stable motor performance, the quality of packaging or labeling output would be compromised.
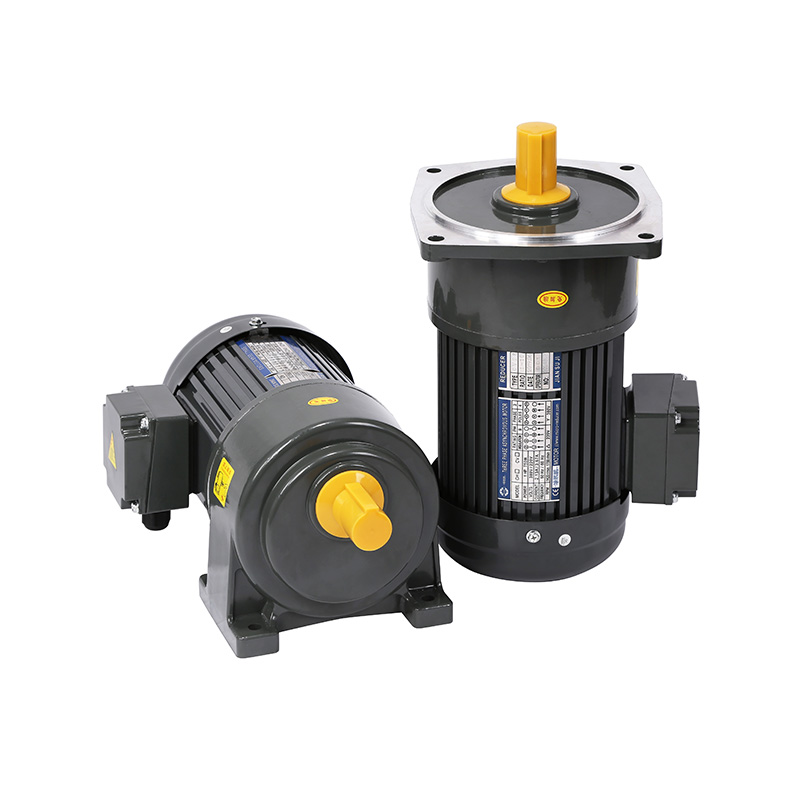

The CI flexo printing machine places additional demands on motor systems. Its central impression drum supports multiple color stations positioned around a single rotating cylinder. This arrangement requires precise torque delivery to maintain consistent pressure across different substrates. The motor must coordinate with other mechanical parts to prevent misalignment and color drift. The accuracy achieved here depends heavily on the combined function of the motor, gear box, and reducer, which together ensure that each rotation maintains reliable speed and torque balance.
Micro motors play an equally valuable role in flexographic printing systems. While larger motors manage the main power output, micro motors are applied to fine-tuning tasks such as plate cylinder alignment, tension adjustments, and web guiding. These functions are critical when working with different substrates, from thin films to corrugated boards. Micro motors make it possible for printers to adjust quickly without major interruptions, adding flexibility to production lines.
The gear box acts as the link between motor power and mechanical movement. Its purpose is to distribute torque effectively while reducing mechanical strain on other components. A well-calibrated gear box minimizes slippage and energy loss, which helps maintain printing consistency and reduces operational costs. In flexo printing environments, where machines operate continuously, the gear box contributes directly to long-term mechanical durability.
The reducer complements these functions by managing speed and torque conversion. In many flexographic printers, reducers allow motors to operate at efficient speeds while delivering the torque necessary to handle large rolls of material or extended production cycles.
These integrated components highlight how motors are not isolated elements but rather part of a complex mechanical system. In flexo printing machines, the motor delivers energy, the CI flexo printing machine requires precise torque application, the micro motor adds fine adjustments, the gear box stabilizes torque transfer, and the reducer balances speed with workload demands. Together, they allow flexographic printing systems to function with reliability and efficiency across diverse production needs.
Future directions for motor applications in printing machinery may include improved energy management, enhanced micro motor responsiveness, and more compact gear box and reducer designs. These developments would help printing machines achieve greater adaptability while maintaining consistent mechanical performance.
The motor, in combination with related components, remains central to the advancement of industrial printing. Their integration with micro motors, gear boxes, and reducers demonstrates how engineering principles sustain operational stability while supporting innovation in printing technology.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى












Contact Us