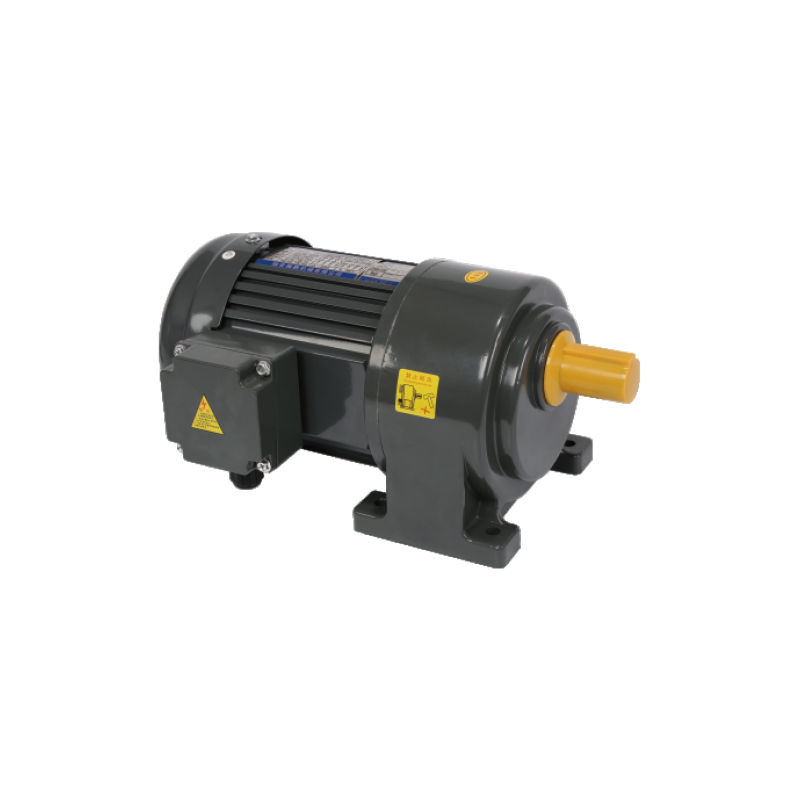
Helical Gear Motor Factory Insights
Helical Gear Motor – Factory Workshop Feedback and Questions
The term Helical Gear Motor stands out in factory automation, material-handling and processing plants where smooth, quiet torque transmission is required. From the workshop floor, an engineer asks: “Is my Helical Gear Motor quieter and more durable than the older spur-gear drive we replaced?” Many operators note quieter operation when replacing straight-cut gear drives with helical-gear motors, although a few also report that the cost of installation or shim and bearing setup was higher than expected.

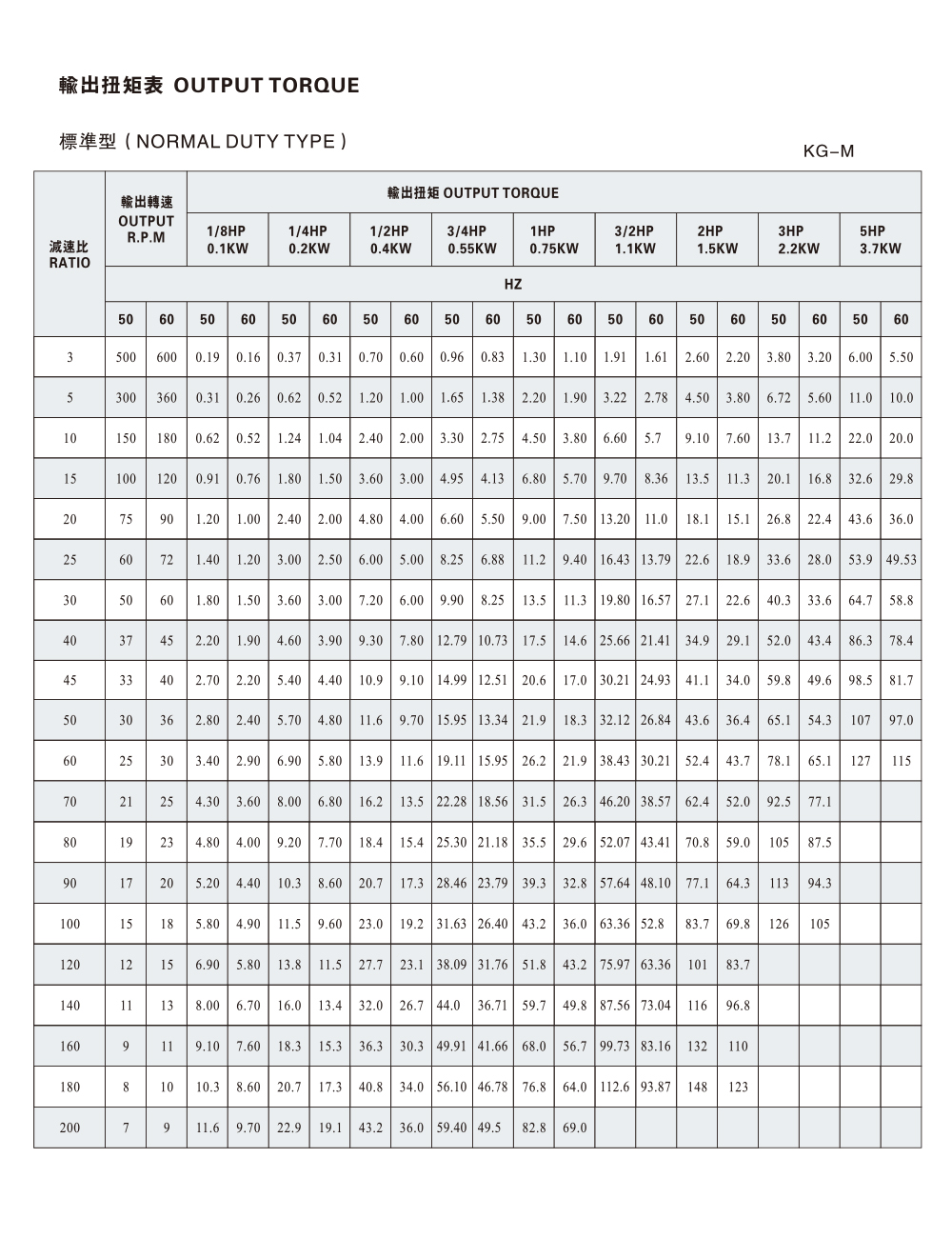
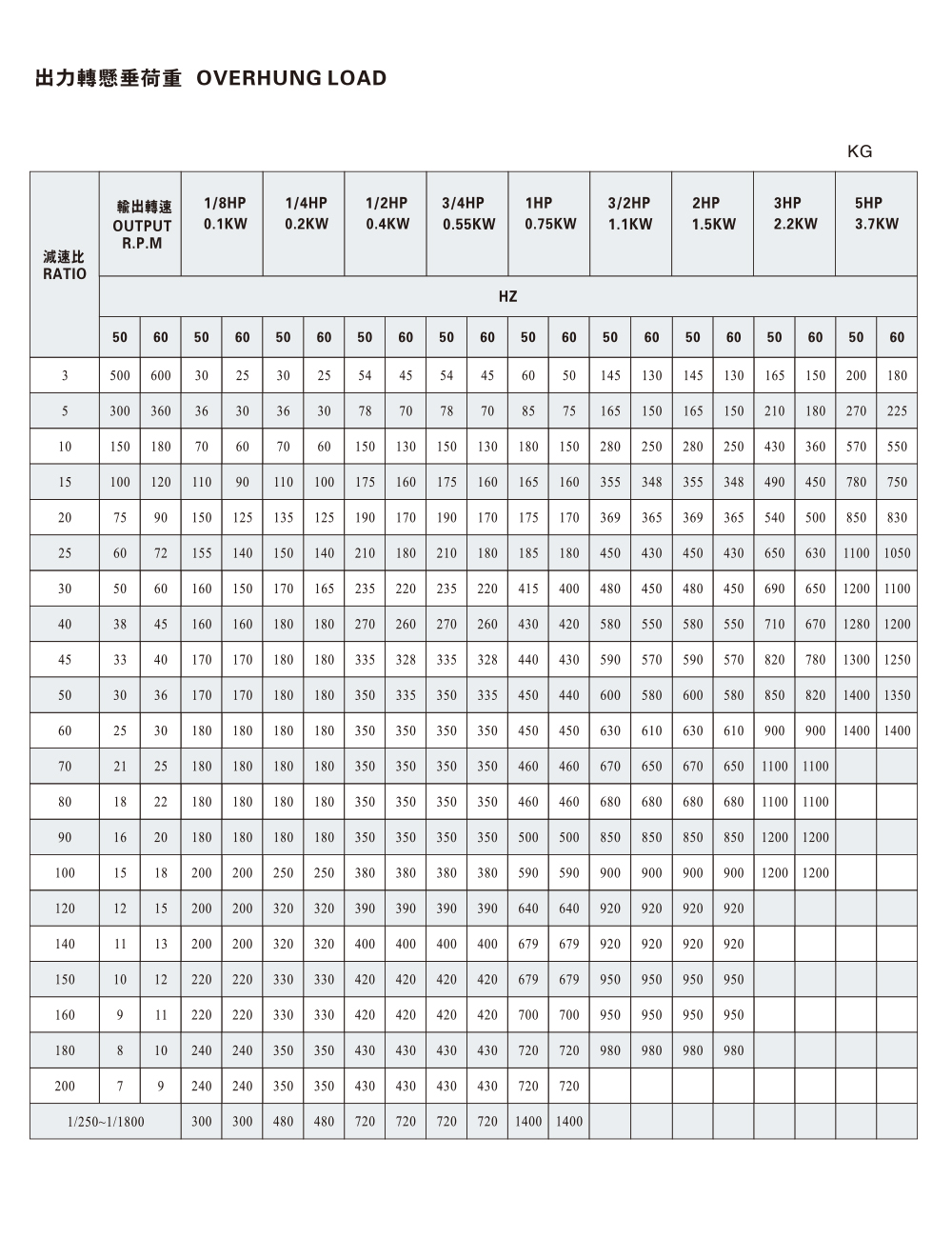
Another factory question: “What helix angle and bearing arrangement does our Helical Gear Motor need to handle our axial-thrust loads?” Bearing selection is flagged as critical when helical gearing is used, because angled teeth introduce axial loads in addition to radial loads inside the gear motor unit.
Helical Gear Motor – How do industrial users compare it to spur/ worm gear motors?
In production environments, the choice among gear motor types often hinges on trade-offs. For helical gear motors:
- They offer a larger tooth-contact area than spur gears, which typically lowers vibration and noise in heavy-duty machinery.
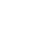
- Efficiency remains strong: industrial helical geared motors report nominal input power ranges from 0.12 kW up to 200 kW and maximum torques up to 100,000 N·m in some series.
- By comparison, worm-gear motors sacrifice some efficiency to gain self-locking, but in factory conveyor or mixing service many plants prefer higher efficiency and lower heat.
Helical Gear Motor – Installation, bearing and load-handling issues in production lines
Factory maintenance records show that proper bearing arrangement and mounting rigidity are key for a helical gear motor. One technical article indicates that bearing layout and arrangement have big impact on durability when helical gears are used. Axial forces induced by helix angle must be managed with thrust bearings or integrated bearing configurations. Many plant engineers ask: “What bearing specification should I use for our new helical gear motor given our load and duty cycle?”
Another common production-floor question: “We have helical gear motors on our mixers and conveyors – why is one unit showing increased backlash after 6 months?” In many cases the fault traced to misalignment, inadequate lubrication, or a housing flexing under load, rather than the gear design itself. For example, in heavy-duty helical geared motor units rated for output torque up to 20,000 N·m in cement or pulp-and-paper plants, servicing intervals were shortened when installation support was inadequate.
Helical Gear Motor – Specification benchmarks and what factories are seeing
For procurement and engineering teams specifying a Helical Gear Motor today, some benchmarks provide guidance:
- Rated input power: 0.12 kW up to 200 kW in many standard parallel-shaft helical gear motor series.
- Maximum torque: units reaching up to 100,000 N·m (in cast-iron housing, modular design) are available.
- Gear ratios: typical helical gear motor modules enable reduction ratios (input to output) across the range of a few times (e.g., 4 : 1) up to very large reductions (hundreds : 1) depending on multi-stage units.
- Efficiency: Heavily loaded helical gear motors in industrial use exhibit efficiency often above 90%, sometimes slightly lower if axial thrust and sliding contact are large.
When comparing, if a worm gear motor delivered 300 N·m at 500 rpm, a helical gear motor of similar size might deliver 350 N·m at 600 rpm with lower noise and lower temperature rise, but may cost somewhat more and require more precise mounting.
Conclusion
The Helical Gear Motor remains a strong industrial solution for factories seeking quiet, high-torque, efficient gear drives in conveyors, mixing, material-handling and processing equipment. Engineering teams should pay special attention to helix angle, axial thrust bearing arrangements, mounting rigidity and lubrication intervals. Compared to older spur-gear or worm-gear motor setups, helical gear motors offer measurable benefits in noise reduction, operational stability and often improved efficiency.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى












Contact Us