Compact Gear Motor Drives Next-Gen Robotics Growth
In recent years, Compact Gear Motor has gained strong attention in automation and robotics. The need for smaller, lighter, yet powerful motion systems fuels interest in compact gear units that fit tight spaces yet deliver required torque.
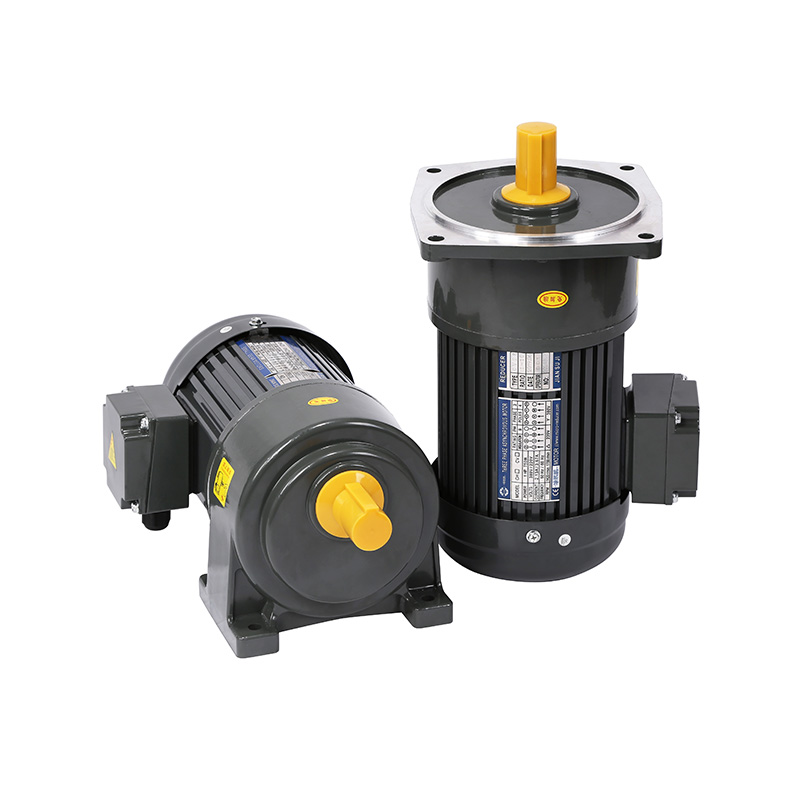
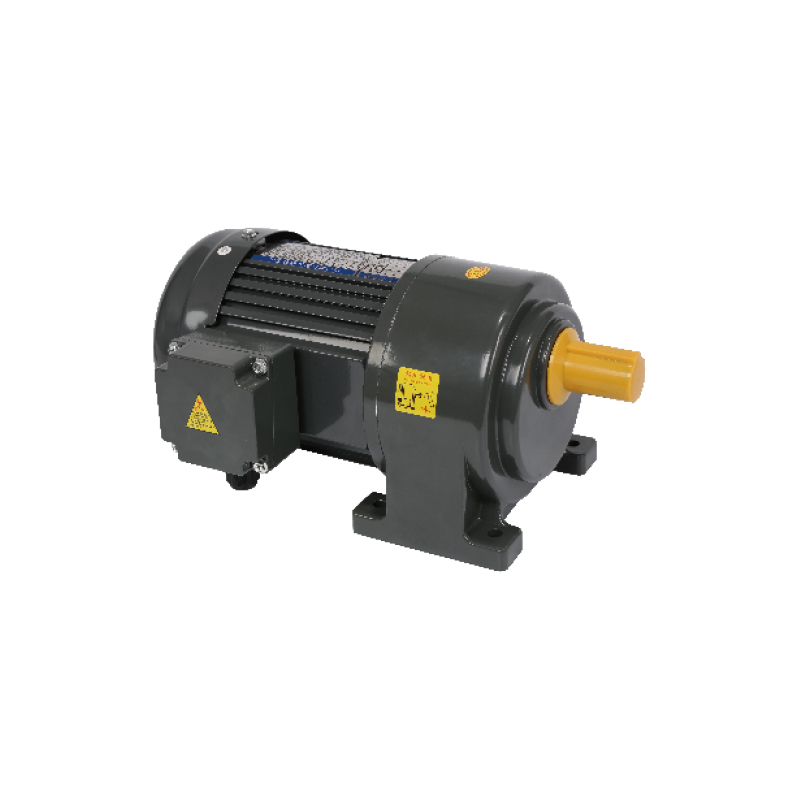
These motors help machines perform precise motion control while saving space. Many automation designers now adopt smaller gear motors that integrate motor and reduction gear into a compact package, enabling seamless embedding into robots, conveyors, actuators, and other systems that demand efficiency in constrained layouts.
Compact Gear Motor High-Torque & Compact Design Trends
One major trend centers on achieving high torque in compact design. Advances in gearing ratios, gear pairing, and internal geometry allow compact motors to output higher torque without growing bulk. Engineers adopt techniques such as multi-stage gearing, optimized tooth profiles, and high-grade materials to boost torque density.
Compact gear motors now appear in applications once reserved for larger drives. For instance, tight-enclosure robotic arms, miniature conveyor modules, and precise indexing systems all employ compact units. The pressure is strong on manufacturers to reduce size while maintaining power. The modern compact gear motor is expected to deliver strong torque even at low speeds, suited for many motion tasks.

Compact Gear Motor Smart Features & Sensor Integration
Another key evolution is embedding smart features. Compact gear motors increasingly include sensors—for temperature, vibration, torque load—and communicate status to control systems. Real-time monitoring helps detect wear, overload, or misalignment early. That capability reduces unplanned downtime and supports preventive maintenance.
Connectivity options such as CAN, Modbus, or digital interfaces allow gear motors to join broader automation networks. In factories that pursue Industry 4.0 standards, compact gear motors act as “smart nodes” in motion control. Such integration supports centralized monitoring, adaptive speed control, and coordinated system behavior.
Compact Gear Motor Material & Manufacturing Upgrades
Materials and manufacturing techniques drive performance improvements. Use of higher strength alloys, better bearing materials, improved lubricants, and advanced surface treatments extends life and reduces friction losses. Manufacturers now enable finer tolerances in gear teeth, better balancing, and tighter assembly control.
Production lines evolve too. Automated machining, precision grinding, robotic assembly, and quality scanning help maintain consistency across many units. That ensures that even in compact designs, reliability and repeatability hold firm.
Compact Gear Motor Market Growth & Competitive Landscape
The compact gear motor sector benefits from overall gear motor market growth. The broader gear motor market shows significant scale expansion, driven by automation, robotics, and industrial upgrades. Compact variants capture a rising share, since many emerging applications favor small, integrated motors.
Competition intensifies regionally. Some countries lead in innovation and production, especially where automation and electronics industries cluster. Manufacturers compete on efficiency, torque density, lifecycle, price, and smart feature integration. To attract customers, many gear motor firms highlight modularity, customization, fast delivery, and after-sales support.
Demand also comes from secondary markets—automated retail systems, conveyor modules, packaging machines, smaller factory lines, lab automation. These use cases often require mid-power, compact motors that are easy to mount and integrate.
Conclusion & Product Recommendation
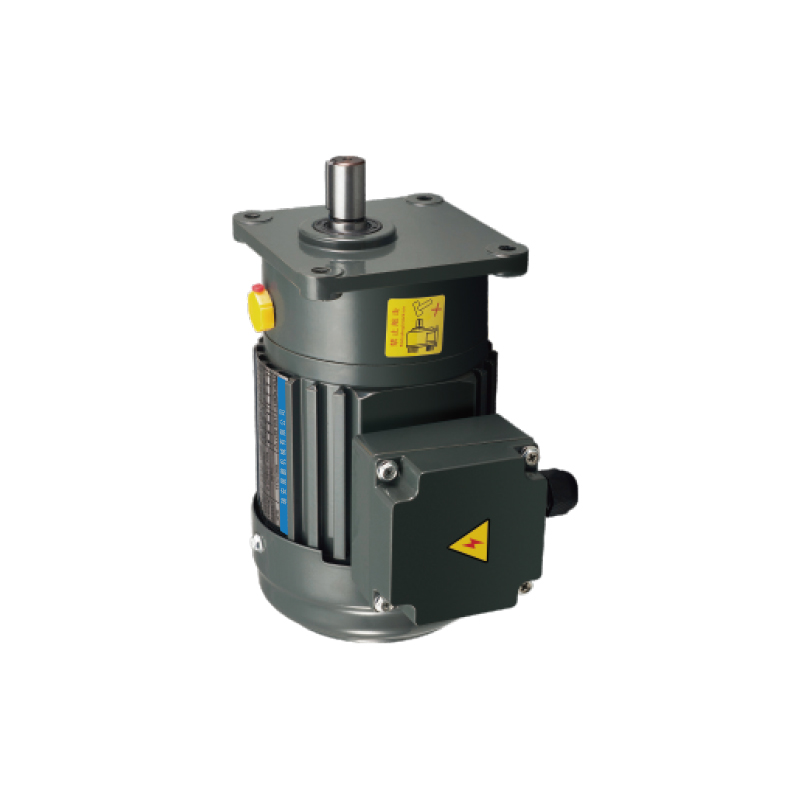
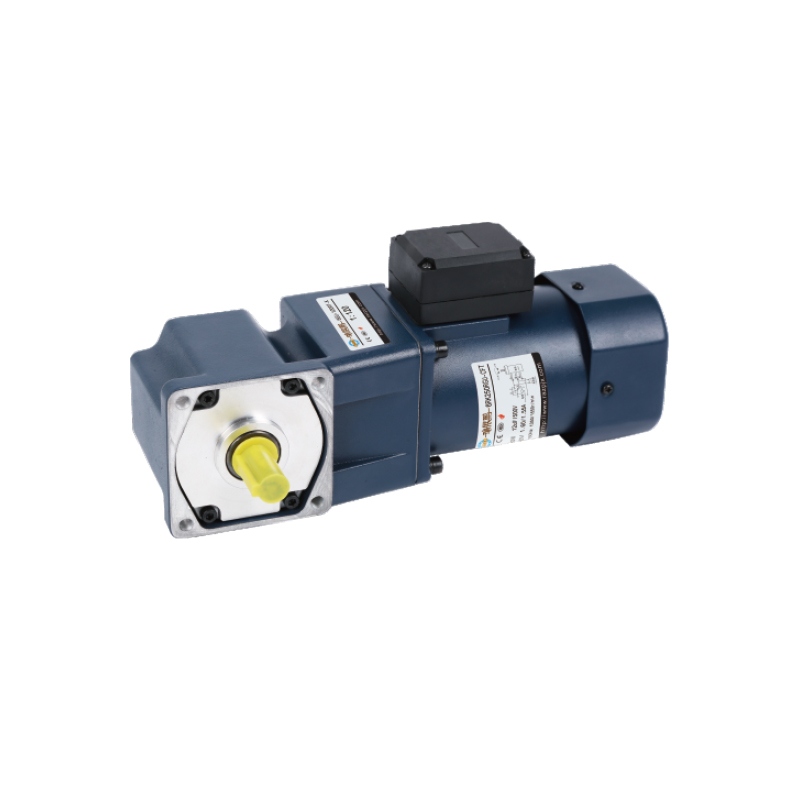
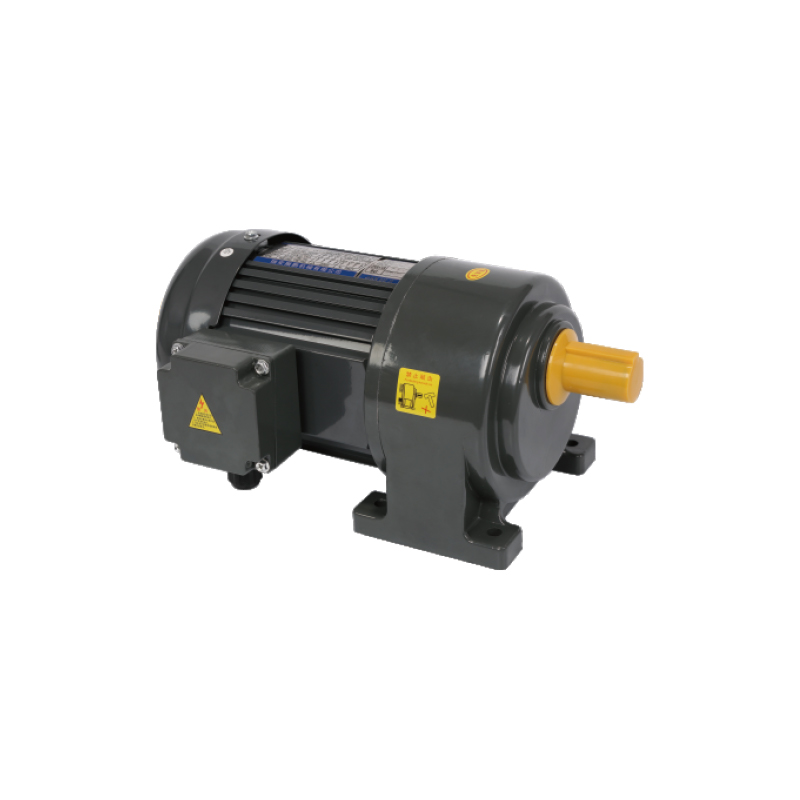
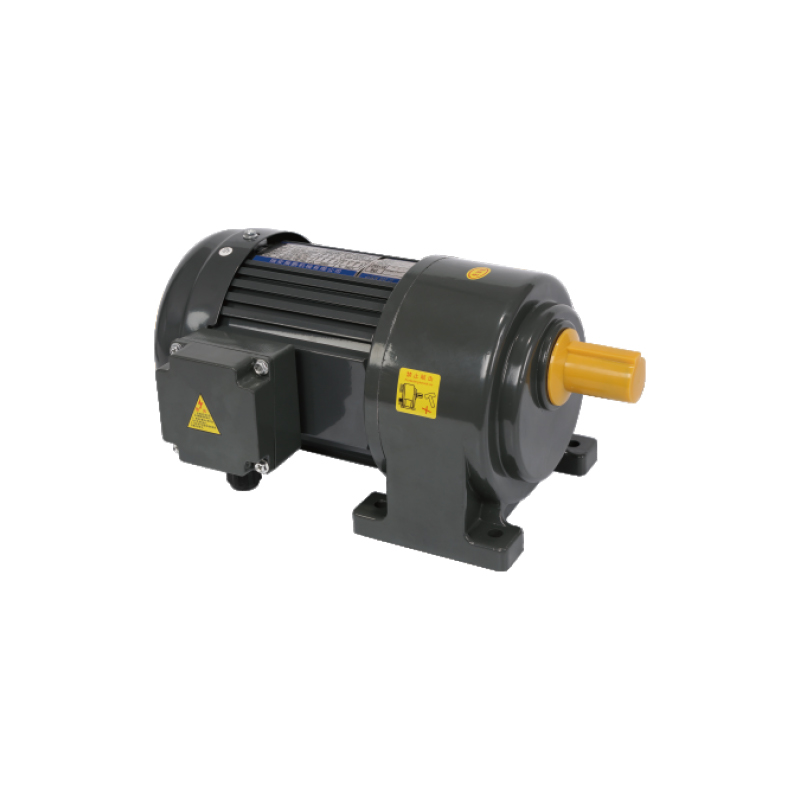
Compact Gear Motor is no longer a niche item—it plays a central role in designing next-generation automated systems.For users seeking a dependable yet compact option in three-phase systems that includes braking function, the 0.1 kW Aluminum Plate 3-phase (Brake) Gear Motor presents a solid choice.
For more detailed product information, please consult Zhanpeng Company.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى













Contact Us