Gear Motor Role in Conveyor and Packaging Systems
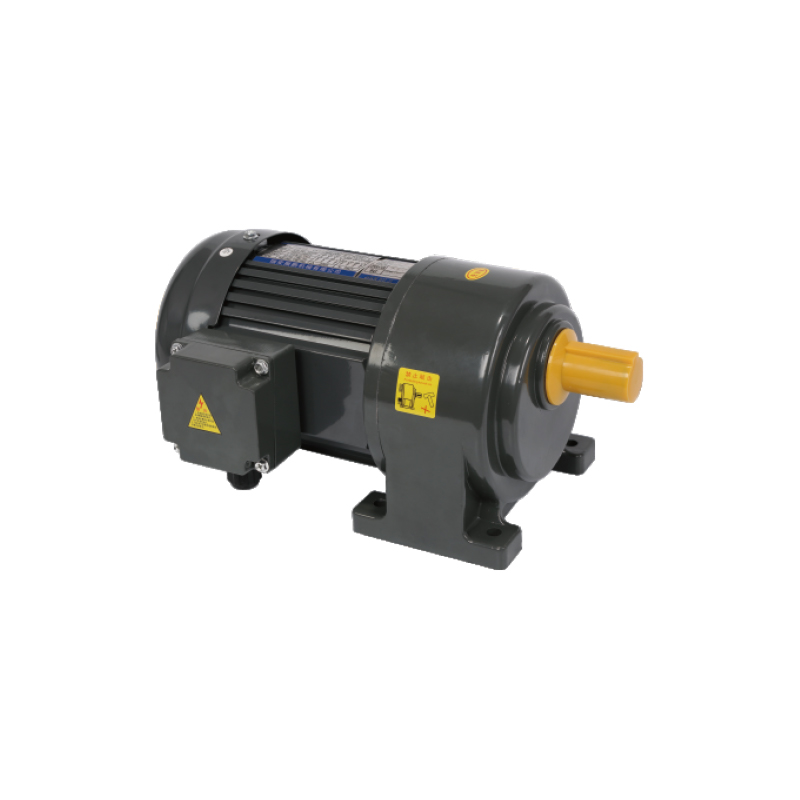
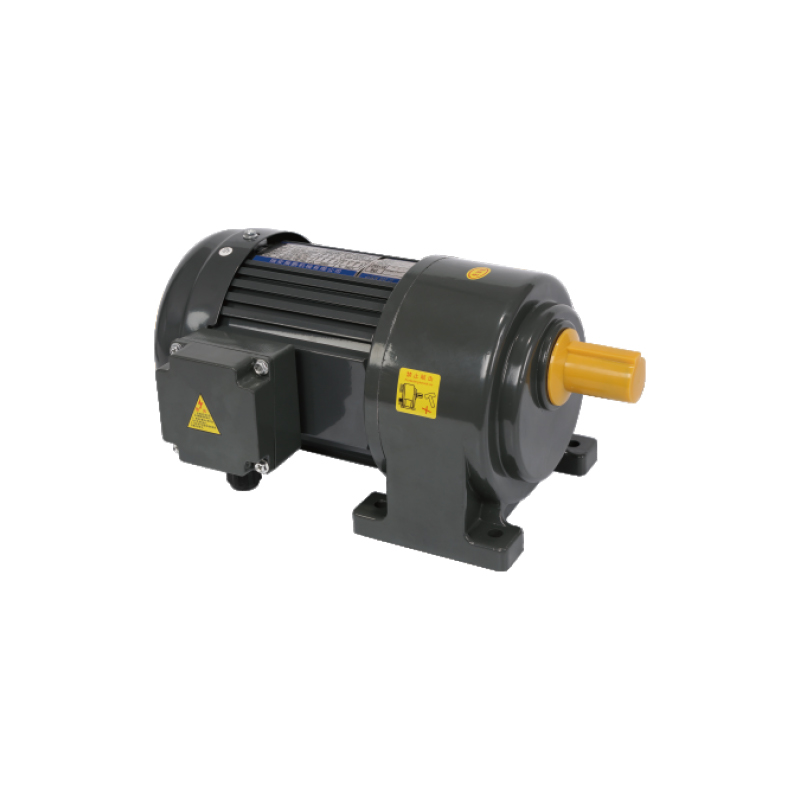
Packaging Machine Gear Motors are central to modern conveyor and packaging systems, providing precise torque output and speed control that supports a wide variety of automated operations. These gear motors enable consistent motion across conveyor belts, sorting lines, rotating machinery, and roll-film or wrapping equipment, ensuring smooth product flow and accurate material handling.

In typical packaging systems, conveyor belt gear motors often operate with a rated torque between 5 Nm and 50 Nm and speeds ranging from 10 RPM to 150 RPM, depending on the type of product and line configuration. High-precision gear motors are frequently used for applications that require controlled acceleration and deceleration, allowing packaging lines to maintain product alignment and reduce mechanical stress on belts and rollers. Motors with integrated planetary or helical gears help improve efficiency, with typical gear ratios between 10:1 and 50:1, enabling smooth transmission of force while maintaining compact motor dimensions.
Beyond standard conveyor belts, gear motors play a critical role in sorting and indexing systems. In these applications, the torque output is carefully matched to the mass of products being handled. For small to medium containers, gear motors delivering 3–10 Nm torque at 20–50 RPM allow for precise product positioning without overloading the mechanical components. For heavier packages, motors with 50–80 Nm torque are used to ensure consistent movement along diverging lines or sorting tracks. Accuracy within ±0.5 degrees of rotation is often required for labeling and filling stations.
Rotational machinery, including labeling wheels, capping units, and rotary cutters, relies on Packaging Machine Gear Motors to maintain uniform speed and torque. For example, labeling spindles often require motors capable of 0.2–0.5 kW output at speeds of 30–100 RPM, while capping or sealing heads may need 0.5–1.5 kW with controlled torque between 10 and 30 Nm. These parameters help ensure consistent label placement, container sealing, and material handling without slippage or product damage.
In wrapping or roll-film control, gear motors regulate film tension and rotation. Motors with torque ranges of 5–25 Nm and variable speed control between 10 and 80 RPM allow for uniform wrapping and minimal material waste. Some systems integrate servo-assisted gear motors for even higher precision, adjusting in real time based on feedback from tension sensors or product position detectors.
Gear motors are also essential in filling, dosing, and material cutting processes. In filling applications, gear motors synchronize container movement with dosing mechanisms to control flow rates accurately. For cutting or trimming operations, gear motors with torque of 10–40 Nm and speeds between 20–120 RPM ensure accurate cutting of films, foils, or packaging boards while coordinating with upstream and downstream devices.
Overall, Packaging Machine Gear Motors provide the foundation for reliable and precise motion control in automated packaging systems. Their ability to deliver specific torque, maintain accurate speeds, and integrate with sensors and control systems allows manufacturers to operate conveyors, sorting lines, filling machines, labeling units, sealing and capping equipment, and roll-film or wrapping stations efficiently. By selecting the right gear motor specifications for each function, production lines can achieve consistent product handling, reduced mechanical wear, and smooth coordination across multiple packaging processes.

FAQ
1. What factors should be considered when selecting a Packaging Machine Gear Motor?
Key factors include required torque, rotational speed, gear ratio, motor power, and the type of load being moved. Conveyor belts may require continuous low-speed operation with moderate torque, while rotary cutters or labeling units may need higher precision with controlled acceleration and deceleration.
2. Can the same gear motor be used for multiple packaging functions?
Some gear motors are versatile enough for multiple tasks, but performance requirements such as torque, speed, and duty cycle must match the specific application. For example, a motor suitable for a conveyor may not provide the required precision for a labeling spindle or film tension control.
3. How does gear motor design impact packaging line efficiency?
Motor design, including gear type (helical, planetary, or worm), precision, and torque stability, affects speed control, product alignment, and material handling consistency. Properly specified Packaging Machine Gear Motors reduce mechanical wear, maintain product quality, and improve overall line coordination.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى













Contact Us