Right Angle Gear Motors in Industrial Systems
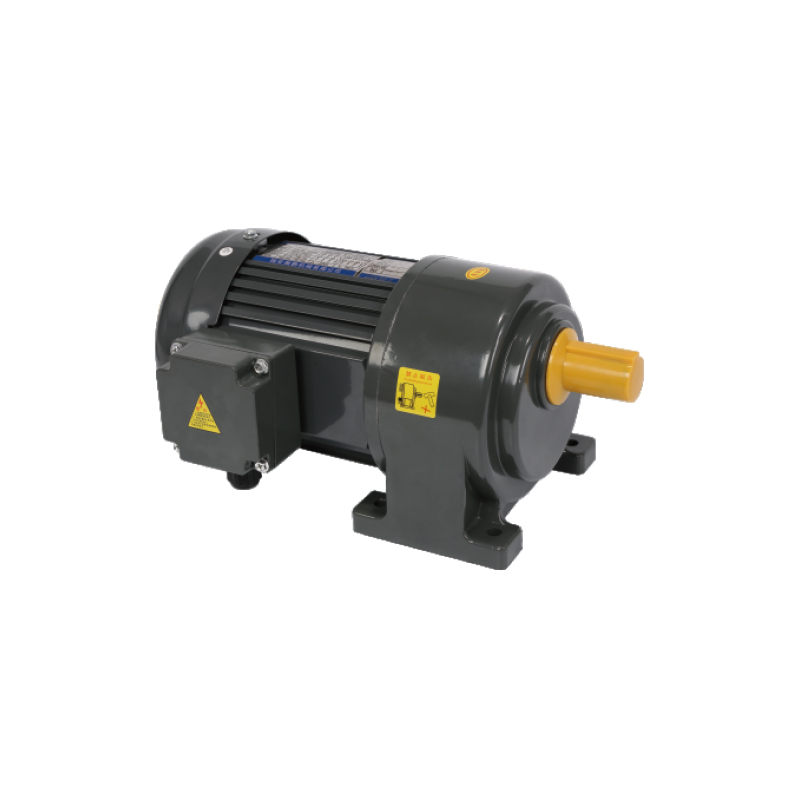
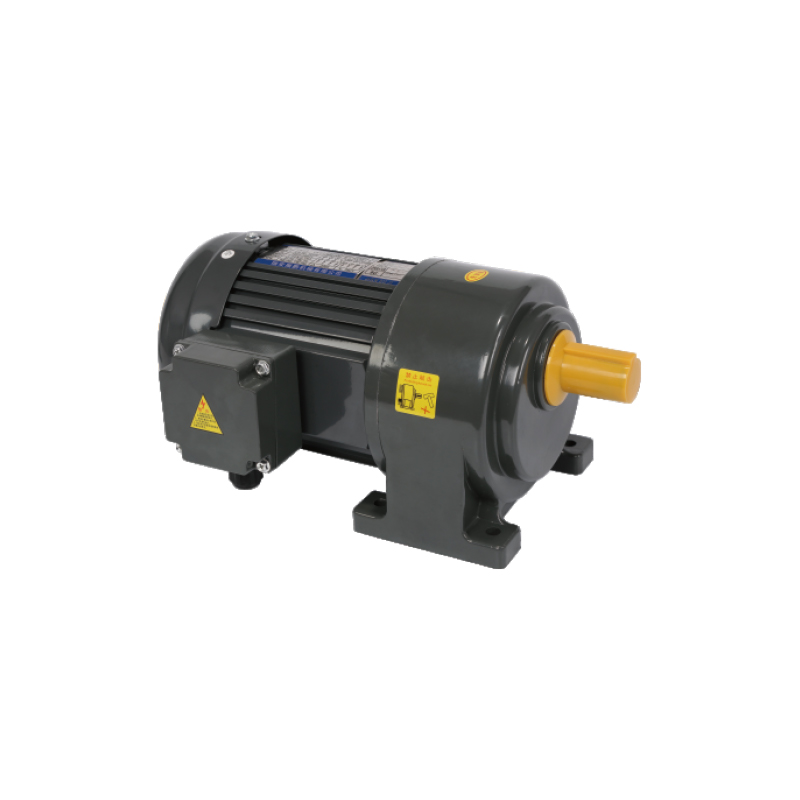
Right angle gear motors are integral components in many mechanical and automation systems. Unlike traditional in‑line designs, these motors position the output shaft at a 90‑degree angle to the motor shaft. This orientation enables compact installation, flexible configuration, and effective torque transmission in space‑limited applications.

Compact Integration and Space Efficiency
One of the main advantages of right angle gear motors is their suitability for tight spaces where conventional motors cannot fit without significant redesign. The 90‑degree configuration allows engineers to align drive elements efficiently within machines, which is especially useful in automated systems with limited installation space. This design also simplifies retrofitting existing equipment by minimizing structural changes.
Right angle gear motors are widely used in conveyor drives, robotic joints, food processing lines, and packaging machines. Their ability to deliver high torque at low speeds while maintaining a small footprint makes them ideal for applications where space and mechanical efficiency are both critical. In robotics, for example, these gear units allow actuators to be mounted close to joint axes, enhancing precision and performance.
Beyond industrial machinery, these motors are often applied in material handling and warehousing systems, where floor space and vertical clearance are limited. Their compact design helps solve engineering challenges where drivetrain components must fit around other system elements.
Precision Motion and Controlled Torque
Right angle gear motors also support precision motion control. Many feature helical or bevel gear sets that provide smooth torque transmission with minimal backlash. Low backlash is essential in equipment where positional accuracy affects overall process results, such as laboratory automation and semiconductor handling.
High‑precision right angle gear motors provide stable torque and repeatable motion, improving system performance. Configurations combined with stepper or servo motors enable intricate movements and calibration routines. Key performance factors include gear ratio, torque output, and vibration levels, which affect efficiency and system longevity. Designs offering high torque density allow smaller motors to achieve required performance, reducing energy use and mechanical stress.
Operational Efficiency and Durability
Operational efficiency is another key benefit. Right angle gear motors balance torque requirements, energy consumption, and maintenance needs throughout their lifecycle. Gear ratios are often tailored for specific tasks, supporting both high torque and controlled speed outputs without overloading the motor or control system.
Durable construction is common in industrial models. Torque ratings range from moderate to high, enabling use from conveyor systems to heavy material handling drives. These motors often feature hardened gears, precision bearings, and optimized lubrication strategies to reduce wear and extend service life. Some include sensors to monitor vibration, temperature, and usage patterns, supporting predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Which industries use right angle gear motors?
A: They are common in manufacturing automation, robotics, packaging, material handling, and food processing due to compact size and effective torque delivery.
Q2: How are they different from in‑line motors?
A: Right angle motors change the power transmission direction by 90 degrees, enabling flexible layouts in constrained spaces, while in‑line motors maintain shaft alignment.
Q3: Can they improve motion precision?
A: Yes. Precision gearing, such as helical or bevel sets, reduces backlash and supports accurate speed and position control in automated processes.
Q4: Are they energy efficient?
A: Modern designs optimize gear efficiency and motor operation. Certain gear types provide higher efficiency than traditional worm gears.
Q5: What specifications should be considered?
A: Key factors include torque, gear ratio, space constraints, environmental conditions, and compatibility with motor type (AC, DC, brushless, or servo).


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى













Contact Us