Waterproof Gear Motor Market Insights and Emerging Trends
Waterproof Gear Motor Overview and Definition
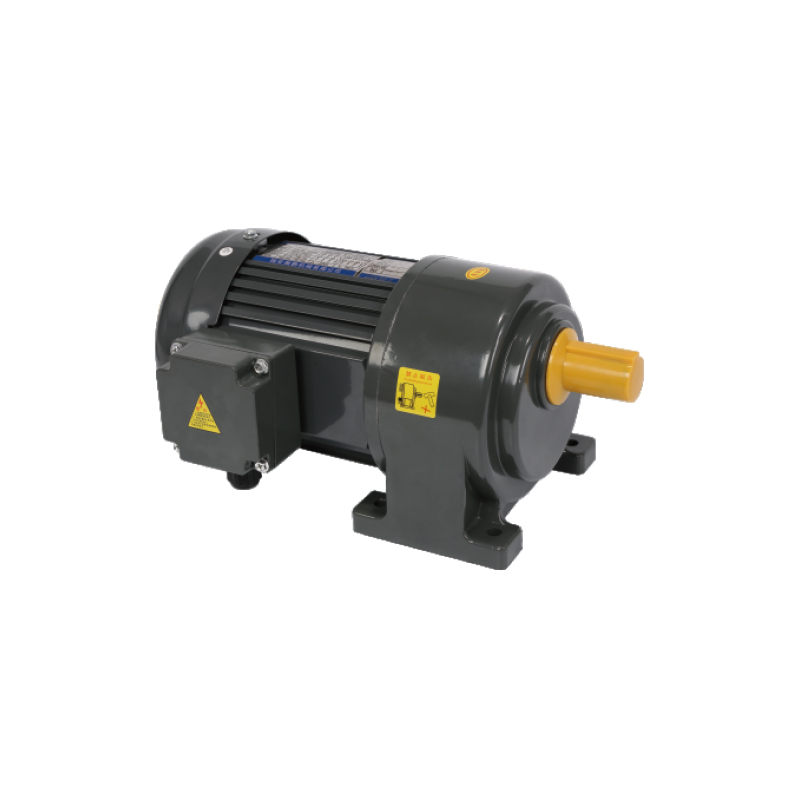
A Waterproof Gear Motor is an electric motor combined with a gearbox that resists the entry of water and dust. Its performance is usually measured by key factors such as torque (Nm), rotational speed (RPM), voltage (V), power rating (W), and ingress protection rating (IP). Industrial models often operate at 12 V or 24 V with torque up to 6 N·m at low speeds, providing dependable output in environments where exposure to moisture or cleaning processes is expected. IP67-rated models are frequently used in sectors like food processing, marine automation, and outdoor robotics.
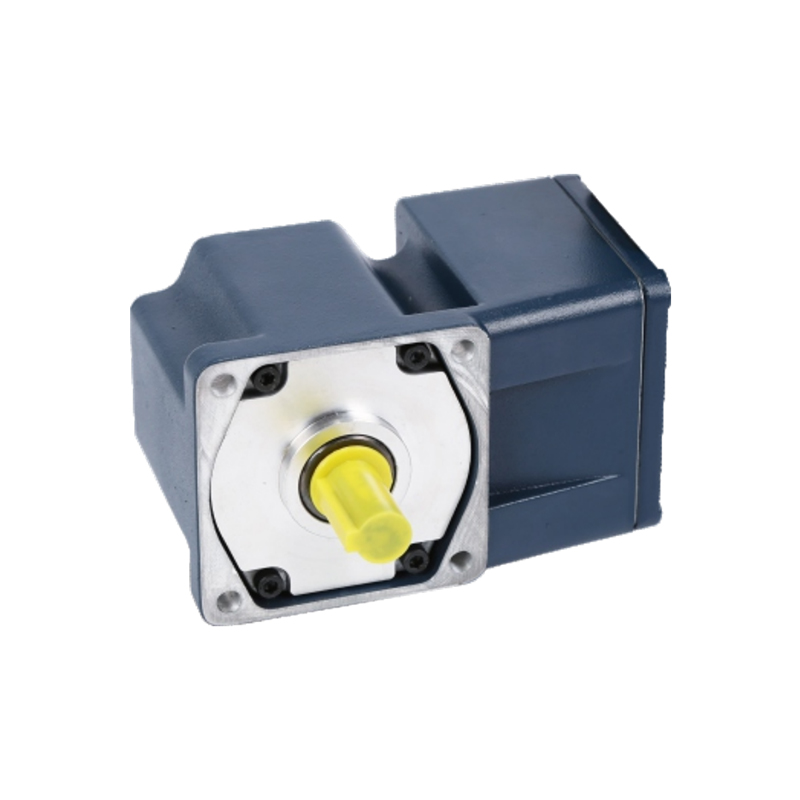

Can a Waterproof Gear Motor Truly Perform Underwater?
A popular question among engineers is whether a waterproof motor can maintain consistent operation while submerged. The answer depends on its structural design and sealing technology. A high IP rating, such as IP67, ensures protection from temporary immersion, while lower classifications may only resist splashing or humidity. Real-world testing has shown that sealing around shafts, bearings, and terminals is critical. Motors designed with precision O-rings, coated shafts, and sealed bearings achieve better endurance, whereas unsealed housings often face corrosion and torque loss over time. This performance gap highlights the need for clarity between “water-resistant” and “fully waterproof” gear motor designs.
QR-Code Integration and Digital Maintenance for Waterproof Gear Motor
Recent product discussions emphasize how digital tools are reshaping motor maintenance. Some manufacturers embed QR codes directly onto the gear motor casing. When scanned, they connect maintenance teams to performance data, torque records, or digital manuals. This approach helps track runtime, lubrication intervals, and environmental performance without opening the housing. For maintenance departments managing hundreds of units, QR-based identification reduces manual record errors and minimizes downtime. The trend indicates that waterproof capability now extends beyond mechanical design toward integrated digital lifecycle management.
Comparing IP Ratings and Performance Data Across Models
Market comparisons reveal several key differences among available Waterproof Gear Motor types.
- IP Ratings: IP67-rated motors can withstand immersion for up to 30 minutes, while IP65-rated models resist water jets but not full submersion.
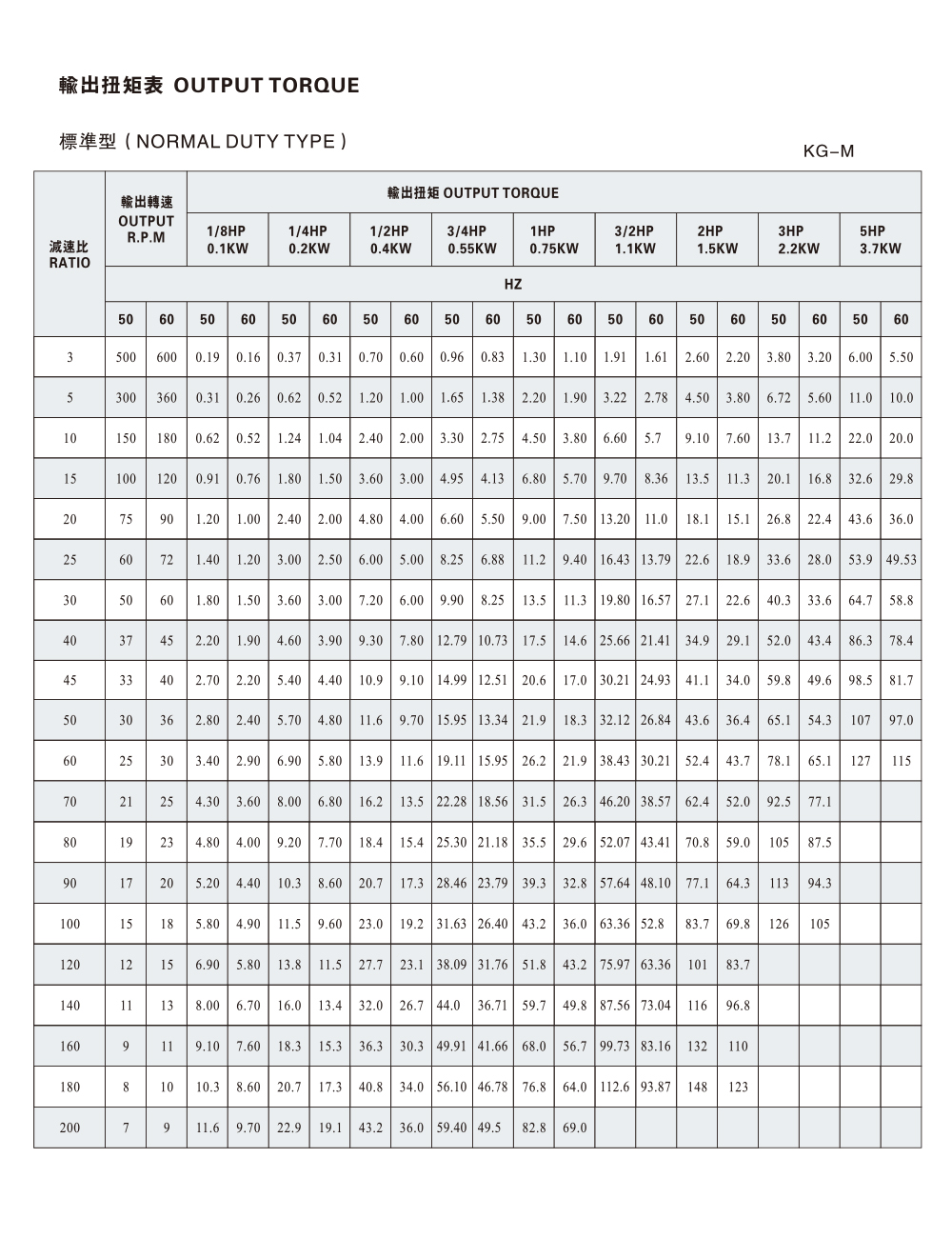
- Torque and Speed: A 12 V DC motor with a 70:1 gear ratio may deliver around 6 N·m torque at 15 rpm. In contrast, compact 37 mm models offer torque near 1 N·m with speed around 20–25 rpm.
- Noise and Efficiency: Industrial brushless designs often operate below 60 dB and achieve higher energy efficiency than brushed versions, though at greater cost.
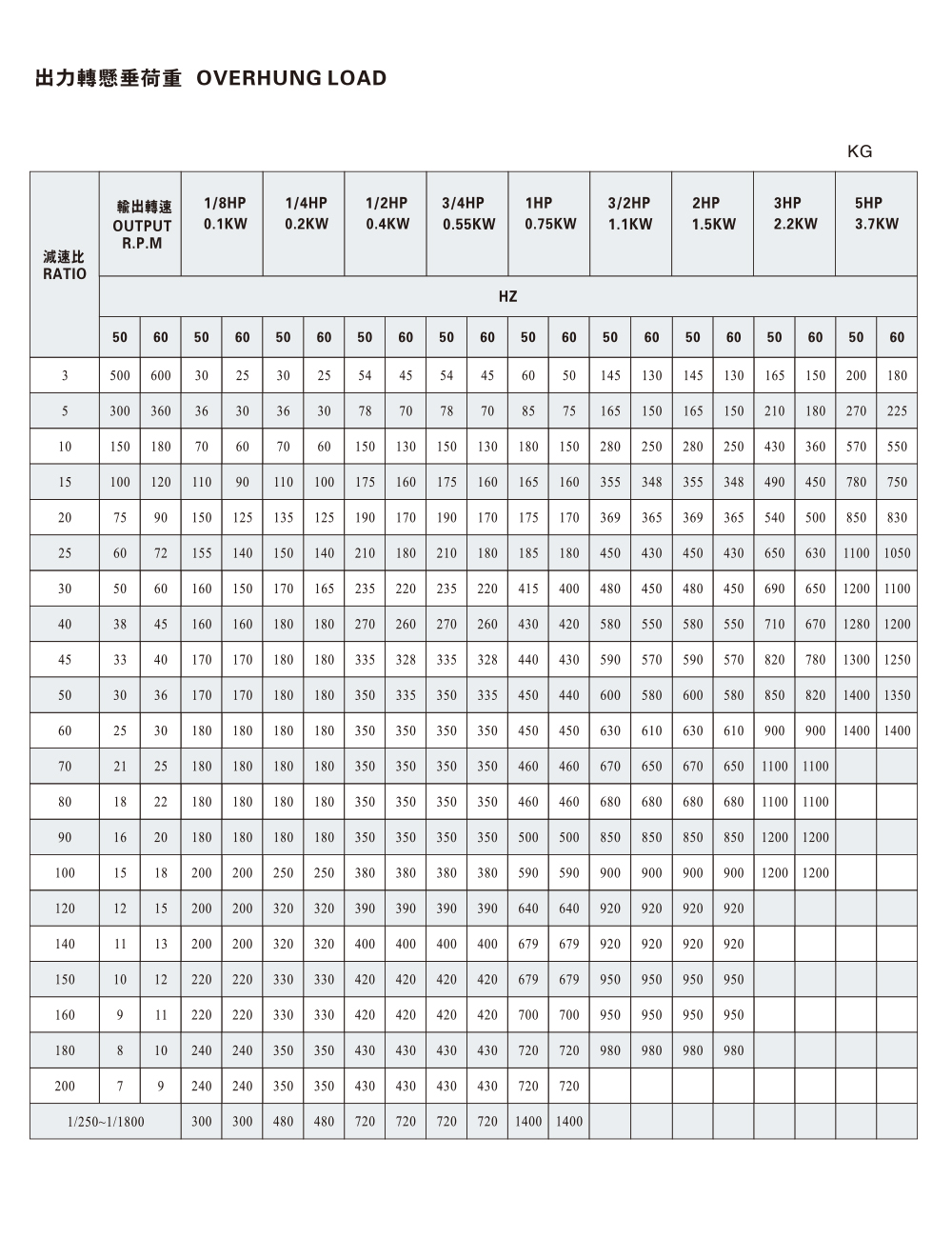
- Thermal Performance: Sealed units reduce airflow and may accumulate heat faster, so thermal balancing through material selection and housing design is crucial.
Such data comparisons clarify how industrial-grade units achieve reliability through defined specifications rather than marketing claims alone.
Expert Insights on Selecting Reliable Waterproof Gear Motors
Experts recommend assessing not just the IP rating but also the sealing technology around moving parts. Shaft seals, terminal gaskets, and housing joints determine long-term protection. Thermal management must also be considered, as completely sealed motors may trap heat during extended duty cycles. Selection should factor in duty hours, environment humidity, cleaning frequency, and expected torque range. In digitally managed plants, combining waterproof hardware with data-encoded QR identification can help streamline predictive maintenance and asset tracking.
Conclusion
The Waterproof Gear Motor represents a growing intersection of mechanical protection, performance efficiency, and digital connectivity. From precise sealing systems to QR-enabled maintenance records, this technology continues to evolve toward greater reliability in challenging environments. Engineers and procurement teams evaluating torque, power, and IP ratings will find that clarity in data and specification transparency are essential for achieving dependable long-term operation.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى












Contact Us