Gear Boxes Maintain Steady Role in Automotive and Industrial Applications
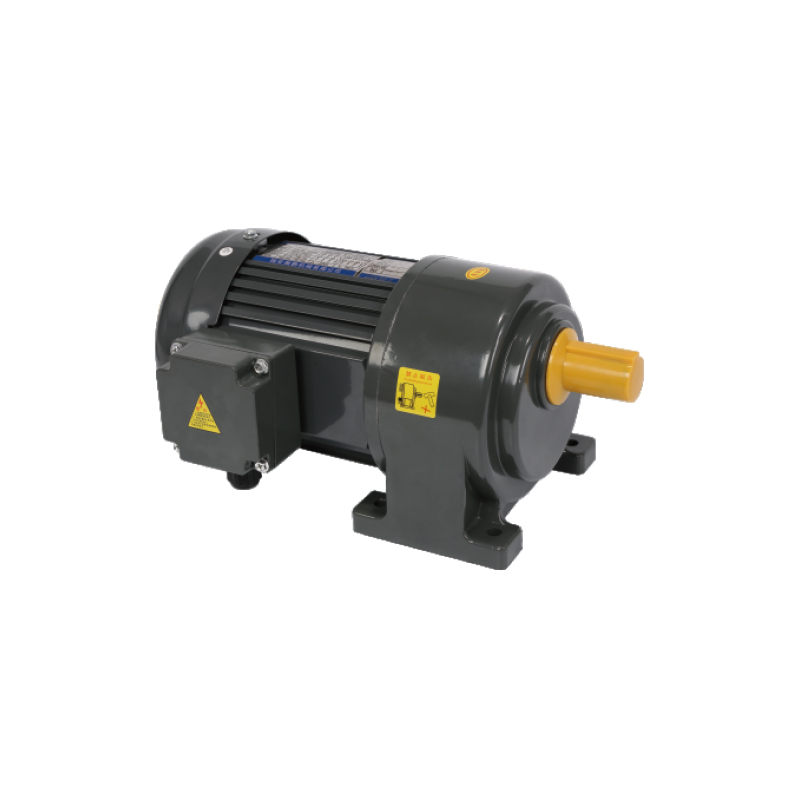
Gearboxes continue to serve as vital components in a wide range of mechanical systems, supporting controlled power transmission and speed regulation across automotive, industrial, and energy sectors. These devices, also known as gear reducers or transmissions, are widely utilized in vehicles, machinery, and renewable energy systems due to their ability to manage torque and adapt motor output to functional requirements. Their versatility and reliability have kept them central to both traditional and emerging engineering applications.
A primary function of gearboxes is to adjust speed and torque between a power source and an output device. By using combinations of gears with different sizes and ratios, gearboxes allow engines or motors to operate efficiently while delivering the appropriate power to wheels, conveyor belts, or other driven components. This capability supports smoother operation and extends the service life of both the power source and the connected equipment.
In the automotive industry, gearboxes are widely used in passenger cars, commercial trucks, and specialized vehicles. They enable seamless gear shifts, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance overall driving comfort. Automatic and manual gearbox designs remain prevalent, each offering distinct benefits depending on the application and user preference. The increasing popularity of electric vehicles has also prompted the development of specialized gearboxes designed to handle the unique torque characteristics of electric motors.
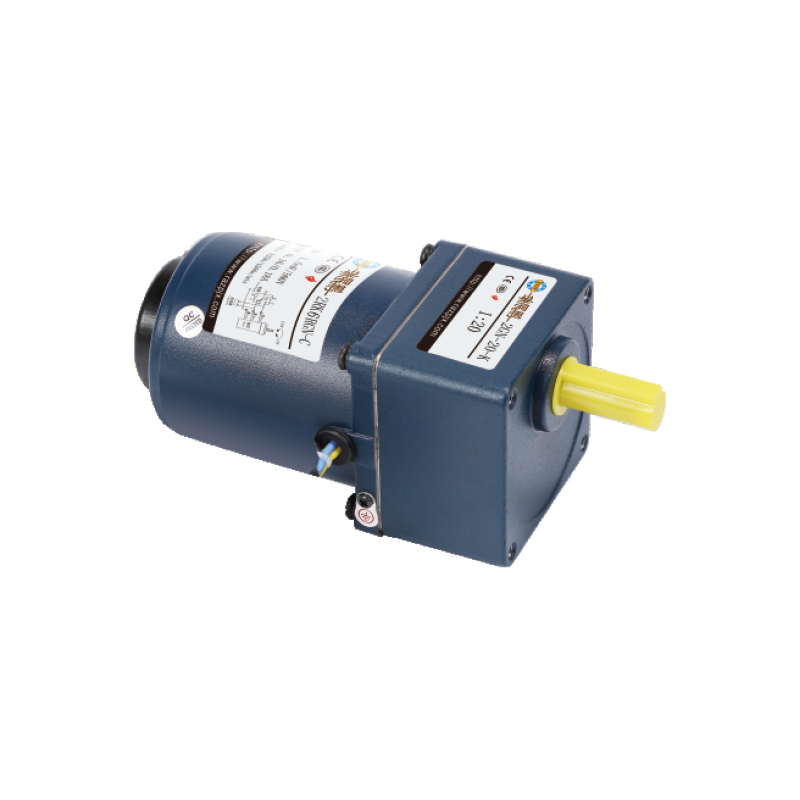
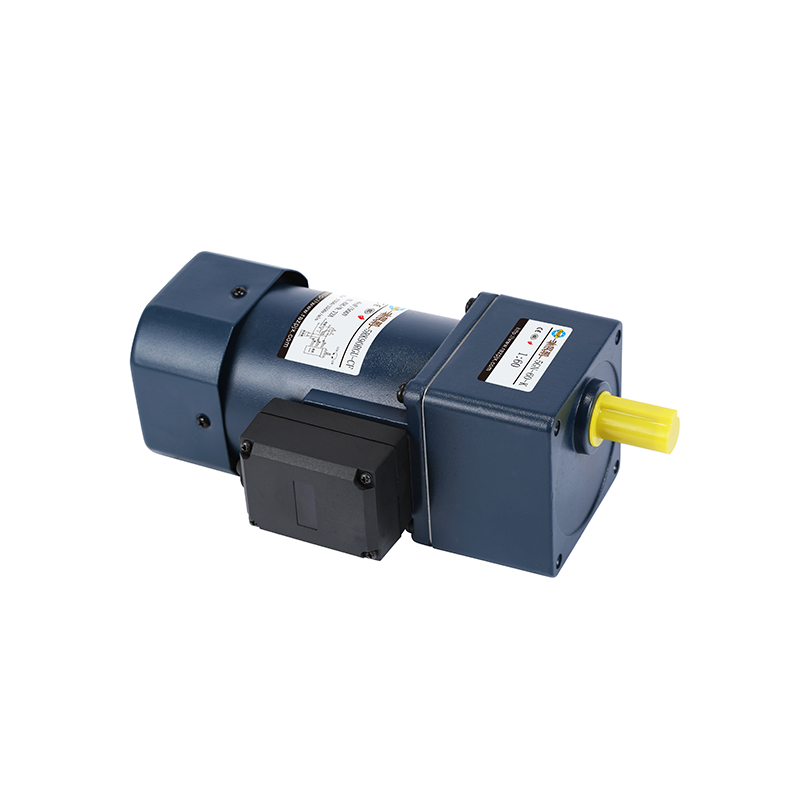
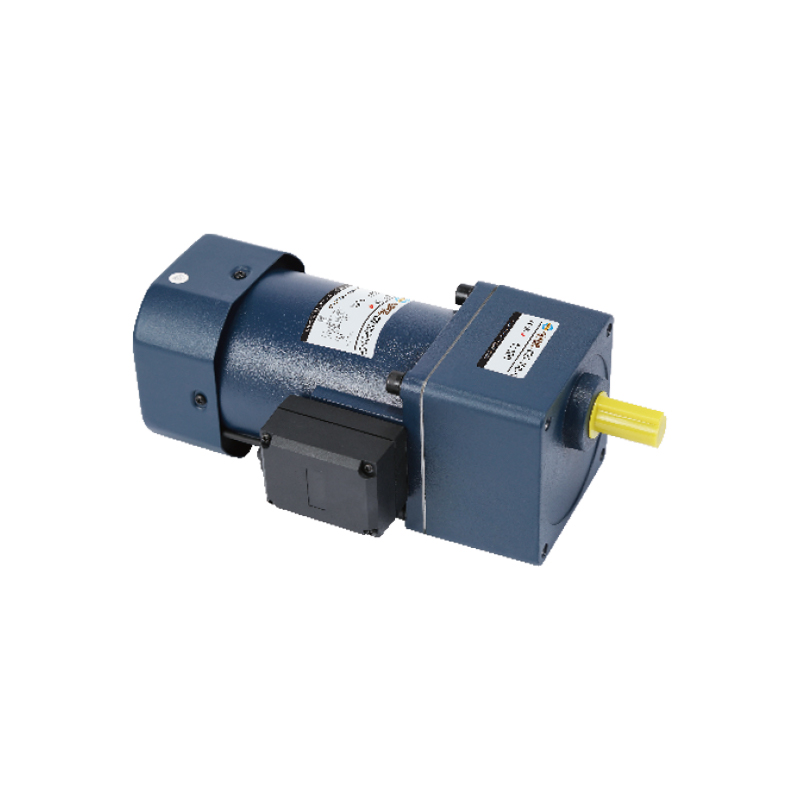
Industrial machinery relies heavily on gearboxes for power transmission in equipment such as conveyors, mixers, and heavy-duty processing machines. Their ability to manage high loads and provide precise speed control makes them essential in manufacturing environments, including food processing, mining, and chemical production. Gearboxes designed for industrial use often feature robust housings and advanced lubrication systems to ensure consistent performance in demanding conditions.
Renewable energy systems, particularly wind turbines, also benefit from gearbox technology. Gearboxes in wind turbines convert the low-speed rotation of turbine blades into higher speeds suitable for generating electricity. This conversion process is critical to the efficiency and reliability of wind energy production, and ongoing improvements in gearbox design continue to support the growth of renewable energy infrastructure worldwide.
Technological advancements have significantly improved gearbox performance in recent years. Enhanced materials, precision manufacturing techniques, and advanced coatings contribute to higher durability and reduced maintenance needs. Additionally, the integration of monitoring sensors allows operators to track temperature, vibration, and lubrication levels, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Sustainability has become a growing consideration in gearbox design and production. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing weight, improving energy efficiency, and utilizing recyclable materials to align with environmental goals. These efforts not only lower operational costs but also contribute to broader initiatives aimed at minimizing the environmental impact of industrial and transportation systems.
Maintenance practices remain critical for gearbox longevity. Regular inspections of lubrication, seals, and gear alignment help prevent premature wear and ensure optimal performance. Advances in synthetic lubricants and sealing technologies have further reduced the frequency of required maintenance, providing additional value to end users in both automotive and industrial settings.
The adaptability of gearboxes to various configurations and applications underscores their enduring relevance in engineering. From compact units for small electric tools to large-scale systems for heavy machinery, gearboxes continue to meet the diverse demands of modern technology.
In summary, gearboxes remain integral to numerous mechanical systems, enabling efficient power transmission and speed control across automotive, industrial, and renewable energy sectors. Their balance of reliability, adaptability, and evolving technology ensures they will continue to play an important role in supporting modern engineering and manufacturing needs.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى













Contact Us