Gear-Motors for Agricultural Applications
Modern agriculture makes greater use of mechanical systems to raise efficiency, precision, and equipment lifespan. A gear-motor is a system that unites an electric motor with a gearbox; this allows machines to deliver motion at controlled speeds while providing enough torque for demanding tasks. Below are seven notable uses of Agricultural machinery gear motors.
- Tractors and Accessory Drives
In tractors, gear-motors are used to power mounted or towed implements. Because implements often require high torque at lower speeds, gear-motors allow the motor to run at its efficient speed, while the gearbox reduces speed and increases torque for the tool. This can improve fuel efficiency, reduce wear on parts, and allow smoother operation when pulling heavy loads or navigating uneven terrain.
- Seeders and Planters
These machines must place seeds at precise intervals and depths. Gear-motors with fine gear ratios, low backlash, and stable rotation help maintain uniform seed distribution even when soil conditions vary. They also allow better control during startup and shutdown, reducing seed bounce, misplacement, or clogging.
- Sprayers
In spraying machines used for pesticides, herbicides, or liquid fertilizers, gear-motors drive pumps, agitators, or nozzle-systems. Because fluid viscosity, pressure, and load can change, gear-motors with consistent torque output and good control help maintain uniform spray patterns.
- Harvesters
Harvesting involves several types of motion: cutting, threshing, conveying, separating. Gear-motors are used to drive cutting blades or heads, feed mechanisms that move crops into separators, and conveyors that carry produce onward. They need to work in dusty, sometimes damp conditions, resist vibration, and accommodate fluctuating loads. Proper gearing helps protect motors from overload and ensures that throughput is reliable and continuous during the harvest season.
- Irrigation Systems
Water delivery requires pumps and valves. Gear-motors can drive pivot arms, open or close valves, or control small pumps for drip systems. Because water pressure changes and power supply may fluctuate, gear-motors that offer consistent torque at lower speeds are useful. They help avoid overwatering or underwatering and enable scheduling or feedback-controlled irrigation.
- Livestock Feeding and Barn Equipment
In livestock farms, gear-motors power feeders, ventilation louvers, barn cleaning systems, and sometimes manure removal equipment. These components often need intermittent operation rather than continuous running, but with capacity to handle heavier loads. Gear-motors with robust gear trains, corrosion-resistant materials, and proper sealing endure exposure to dust, moisture, ammonia, or other agricultural by-products.
- Conveying & Post-Harvest Processing
After crops are gathered, they often pass through cleaning, sorting, grading, and packaging stages. Conveyors driven by gear-motors transport produce; sorters or graders may use gear-motors to adjust incline, speed, or angle. Packaging machines need precise, repeatable motion, which gear-motors can provide.
Key Design Considerations
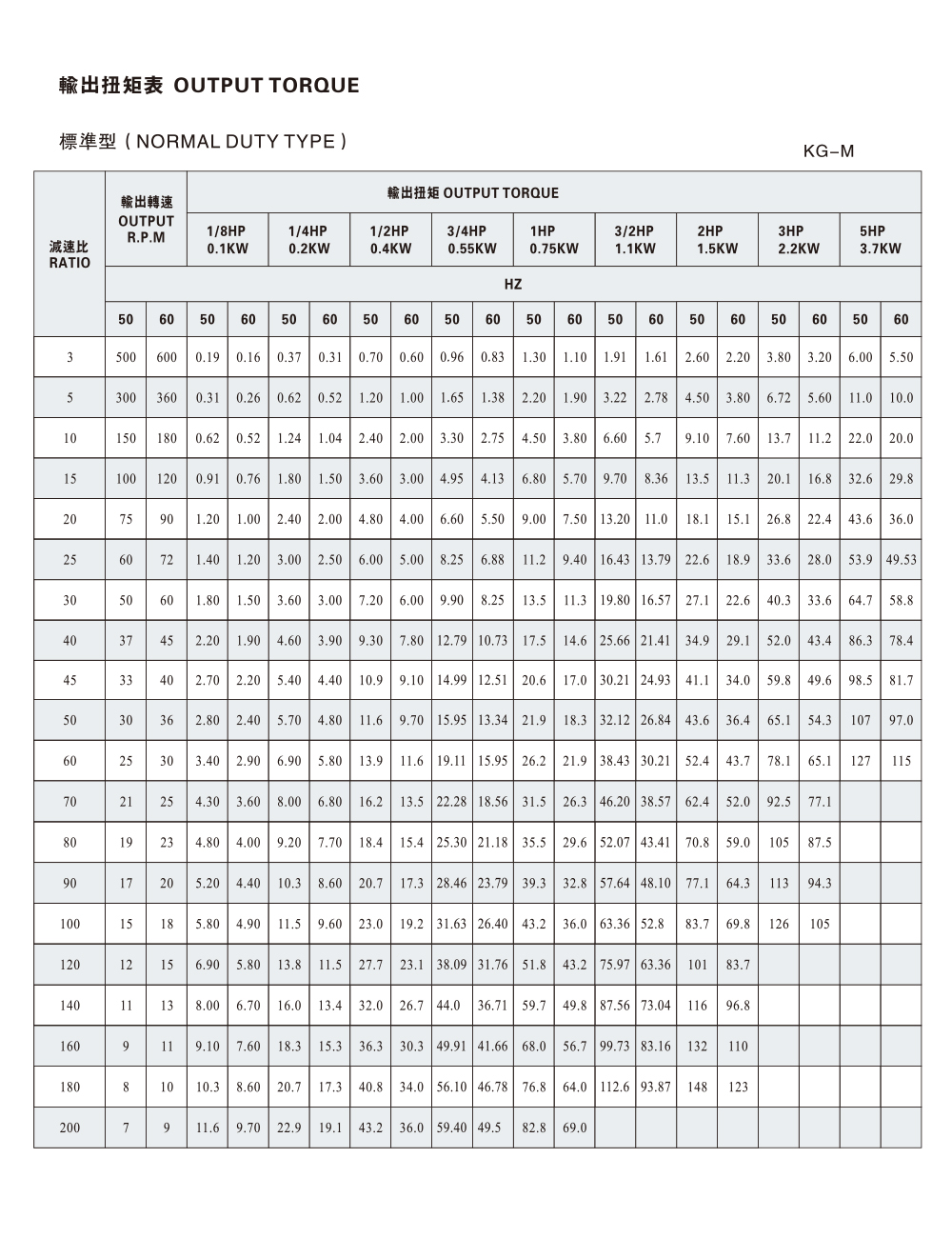
Matching torque and speed with the load and duty cycle so that the gear-motor starts and runs smoothly under realistic field conditions.
Ensuring environmental protection: resistance to dust, moisture, temperature extremes; choosing housings with adequate sealing or IP rating; corrosion-resistant materials.
Considering efficiency, ease of maintenance, gear backlash, lubrication, and tolerance to vibration or shock.
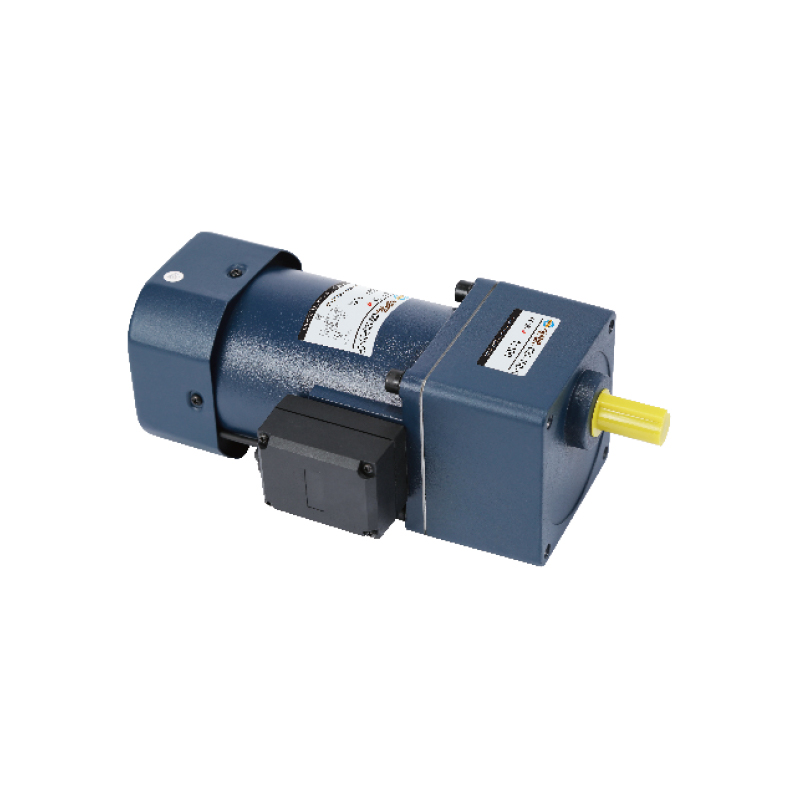
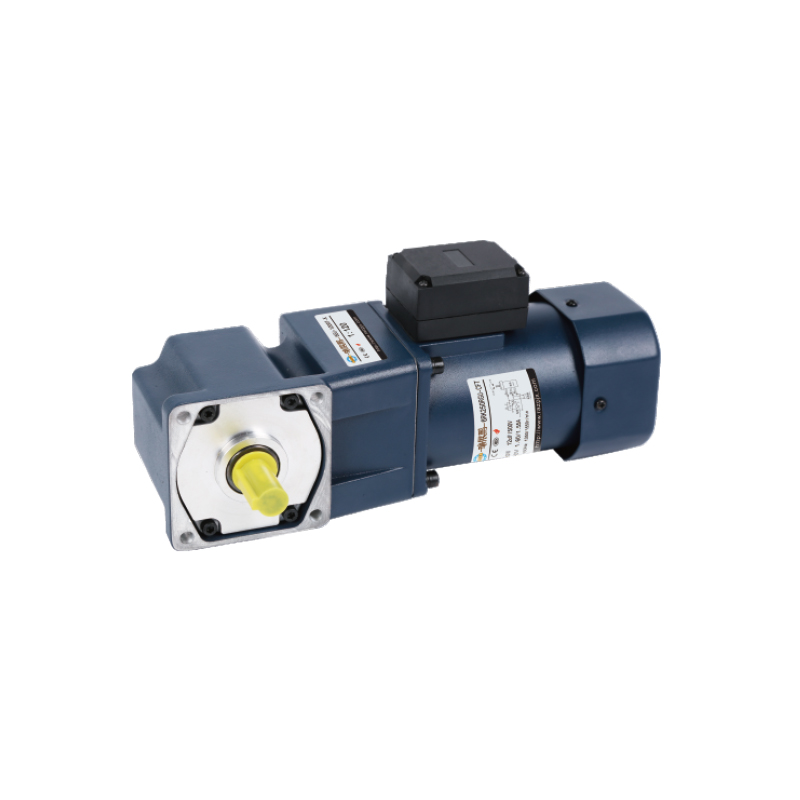
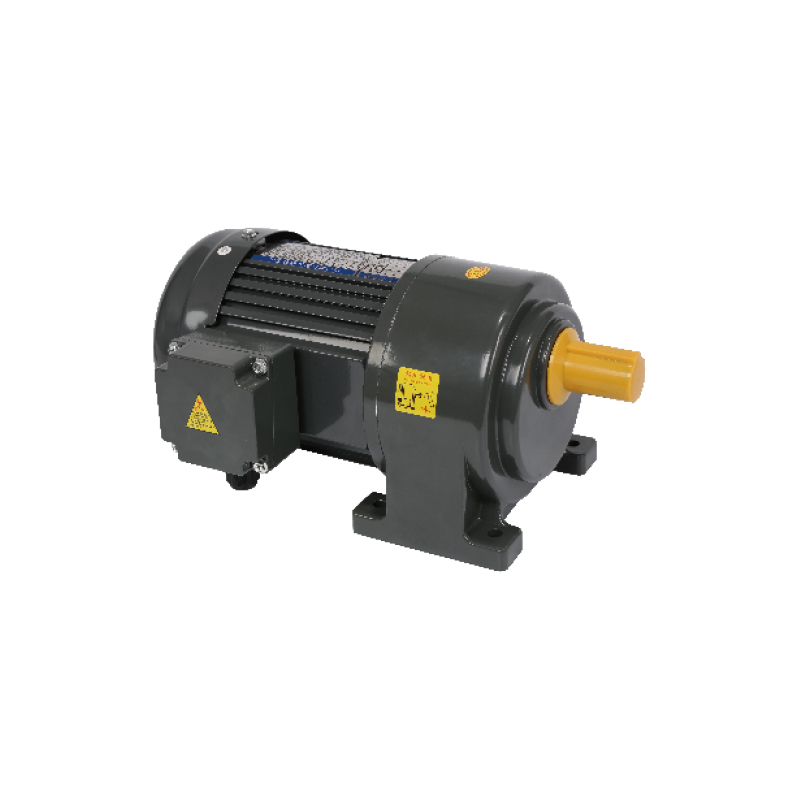
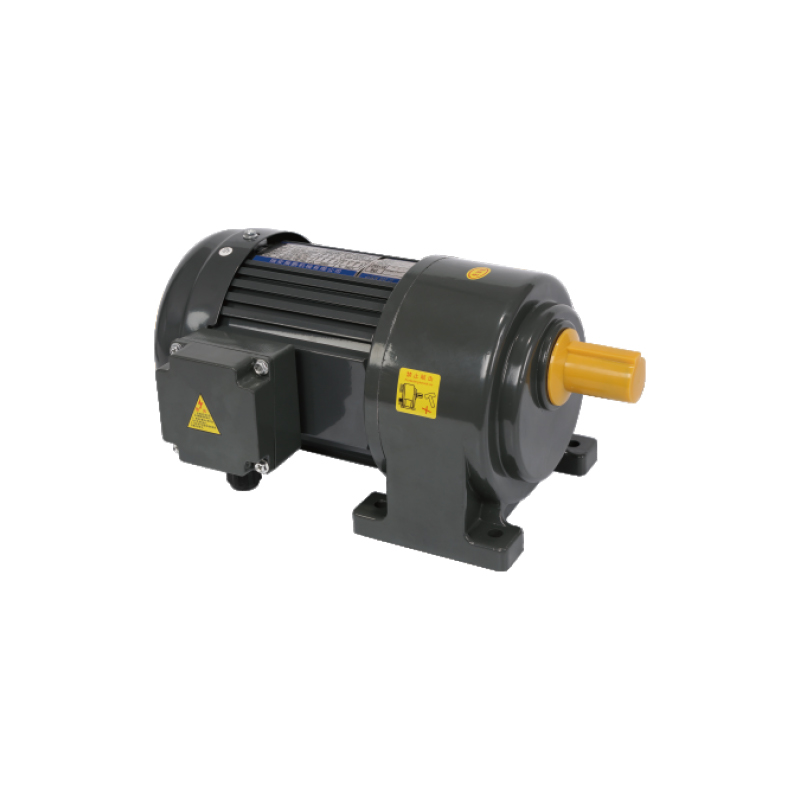
Recommended Product
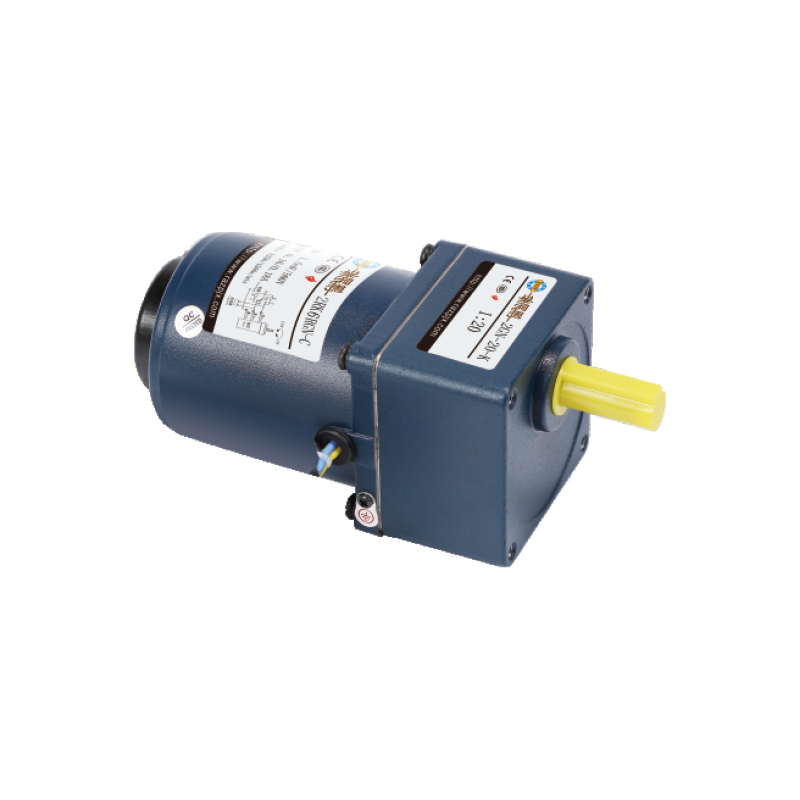

An agricultural machinery gear motor for many of the above agricultural applications is the 60mm 6W/10W High Precision Gear Reducer Motor. It offers:
Output levels of 6 W or 10 W, fitting for small to medium duty tasks.
Frame size around 60 mm, compact yet able to provide useful torque.
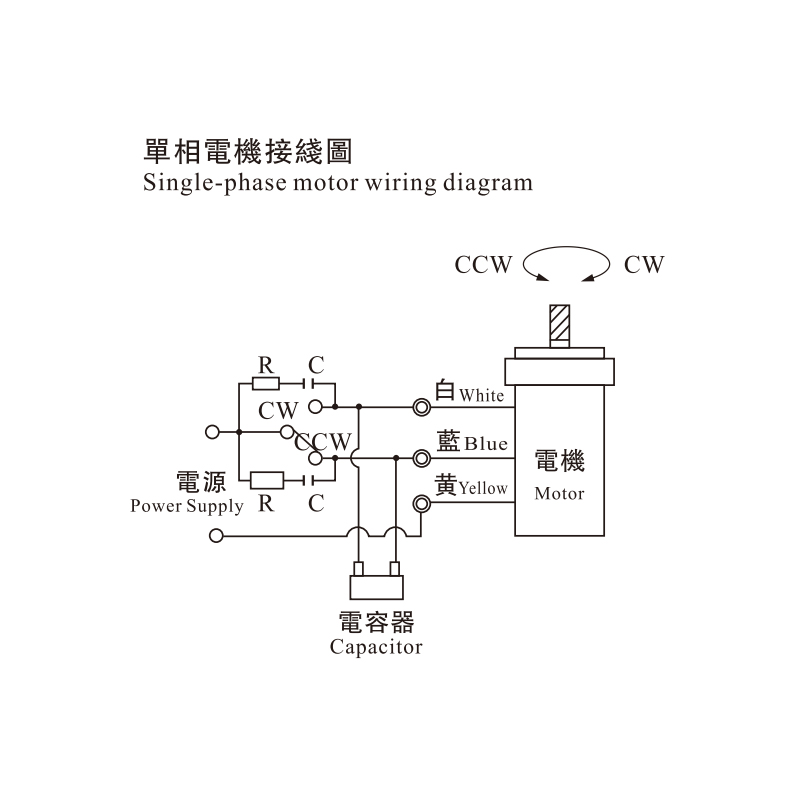
Options for AC voltage levels, with single-phase or frequency variants, and variable speed control.
If you need more detailed information, please contact Zhanpeng Company.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 عربى
عربى













Contact Us